Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Patient Version
General Information About Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
Key Points
- Extragonadal germ cell tumors form from developing sperm or egg cells that travel from the gonads to other parts of the body.
- Age and sex can affect the risk of extragonadal germ cell tumors.
- Signs and symptoms of extragonadal germ cell tumors include breathing problems and chest pain.
- Imaging and blood tests are used to diagnose extragonadal germ cell tumors.
- Some people decide to get a second opinion.
- Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
Extragonadal germ cell tumors form from developing sperm or egg cells that travel from the gonads to other parts of the body.
"Extragonadal" means outside of the gonads (sex organs). When cells that are meant to form sperm in the testicles or eggs in the ovaries travel to other parts of the body, they may grow into extragonadal germ cell tumors. These tumors may begin to grow anywhere in the body but usually begin in organs such as the pineal gland in the brain, in the mediastinum (area between the lungs), or in the retroperitoneum (the back wall of the abdomen).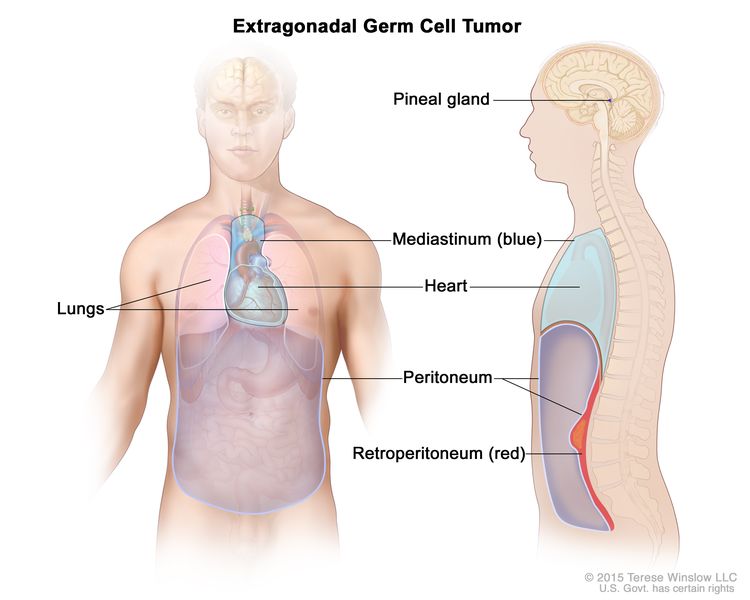
Extragonadal germ cell tumors can be benign (noncancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign extragonadal germ cell tumors are called benign teratomas. These are more common than malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors and often are very large.
Malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors are divided into two types, nonseminoma and seminoma. Nonseminomas tend to grow and spread more quickly than seminomas. They usually are large and cause signs and symptoms. If untreated, malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors may spread to the lungs, lymph nodes, bones, liver, or other parts of the body.
Age and sex can affect the risk of extragonadal germ cell tumors.
Anything that increases a person's chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Not every person with one or more of these risk factors will develop an extragonadal germ cell tumor, and it will develop in some people who don't have any known risk factors. Talk with your doctor if you think you may be at risk. Risk factors for malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors include:
- being male
- being age 20 or older
- having Klinefelter syndrome
Signs and symptoms of extragonadal germ cell tumors include breathing problems and chest pain.
Malignant extragonadal germ cell tumors may cause signs and symptoms as they grow into nearby areas. Other conditions may cause the same signs and symptoms. Check with your doctor if you have:
Imaging and blood tests are used to diagnose extragonadal germ cell tumors.
In addition to asking about your personal and family health history and doing a physical exam, your doctor may perform the following tests and procedures:
- Chest x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
- Serum tumor marker test is a procedure in which a sample of blood is examined to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by organs, tissues, or tumor cells in the body. Certain substances are linked to specific types of cancer when found in increased levels in the blood. These are called tumor markers. The following three tumor markers are used to detect extragonadal germ cell tumor: Blood levels of the tumor markers help determine if the tumor is a seminoma or nonseminoma.
- alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
- beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG)
- lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
- CT scan (CAT scan) uses a computer linked to an x-ray machine to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. The pictures are taken from different angles and are used to create 3-D views of tissues and organs. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
Sometimes a CT scan and a PET scan are done at the same time. A PET scan uses a small amount of radioactive sugar (also called glucose) that is injected into a vein. Then a scanner rotates around the body to make detailed, computerized pictures of areas inside the body where the glucose is taken up. Because cancer cells often take up more glucose than normal cells, the pictures can be used to find cancer cells in the body. When a PET scan and CT scan are done at the same time, it is called a PET-CT.
- A biopsy is the removal of cells or tissues so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. The type of biopsy used depends on where the extragonadal germ cell tumor is found.
- Excisional biopsy is the removal of an entire lump of tissue.
- Incisional biopsy is the removal of part of a lump or sample of tissue.
- Core biopsy is the removal of tissue using a wide needle.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is the removal of tissue or fluid using a thin needle.
Some people decide to get a second opinion.
You may want to get a second opinion to confirm your diagnosis and treatment plan. If you seek a second opinion, you will need to get medical test results and reports from the first doctor to share with the second doctor. The second doctor will review the pathology report, slides, and scans. They may agree with the first doctor, suggest changes or another treatment approach, or provide more information about your cancer.
Learn more about choosing a doctor and getting a second opinion at Finding Cancer Care. You can contact NCI’s Cancer Information Service via chat, email, or phone (both in English and Spanish) for help finding a doctor, hospital, or getting a second opinion. For questions you might want to ask at your appointments, visit Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Cancer.
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
The prognosis and treatment options depend on:
- whether the tumor is nonseminoma or seminoma
- the size of the tumor and where it is in the body
- the blood levels of AFP, beta-hCG, and LDH
- whether the tumor has spread to other parts of the body
- the way the tumor responds to initial treatment
- whether the tumor has just been diagnosed or has recurred (come back)
Stages of Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
Key Points
- After an extragonadal germ cell tumor has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body.
- There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
- Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
- The following prognostic groups are used for extragonadal germ cell tumors:
- Good prognosis
- Intermediate prognosis
- Poor prognosis
After an extragonadal germ cell tumor has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread to other parts of the body.
The extent or spread of cancer is usually described as stages. For extragonadal germ cell tumors, prognostic groups are used instead of stages. The tumors are grouped according to how well the cancer is expected to respond to treatment. It is important to know the prognostic group in order to plan treatment.
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of tumor as the primary tumor. For example, if an extragonadal germ cell tumor spreads to the lung, the tumor cells in the lung are actually cancerous germ cells. The disease is metastatic extragonadal germ cell tumor, not lung cancer.
The following prognostic groups are used for extragonadal germ cell tumors:
Good prognosis
A nonseminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor is in the good prognosis group if:
A seminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor is in the good prognosis group if:
Intermediate prognosis
A nonseminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor is in the intermediate prognosis group if:
A seminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor is in the intermediate prognosis group if:
Poor prognosis
A nonseminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor is in the poor prognosis group if:
- the tumor is in the chest; or
- the tumor has spread to organs other than the lungs; or
- the level of any one of the tumor markers (AFP, beta-hCG, or LDH) is high.
A seminoma extragonadal germ cell tumor does not have a poor prognosis group.
Treatment Option Overview
Key Points
- There are different types of treatment for patients with extragonadal germ cell tumors.
- The following types of treatment are used:
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery
- New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
- High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant
- Treatment for extragonadal germ cell tumors may cause side effects.
- Follow-up care may be needed.
There are different types of treatment for patients with extragonadal germ cell tumors.
Different types of treatments are available for extragonadal germ cell tumors. You and your cancer care team will work together to decide your treatment plan, which may include more than one type of treatment. Many factors will be considered, such as the tumor's prognostic group, your overall health, and your preferences. Your plan will include information about your cancer, the goals of treatment, your treatment options and the possible side effects, and the expected length of treatment.
Talking with your cancer care team before treatment begins about what to expect will be helpful. You’ll want to learn what you need to do before treatment begins, how you’ll feel while going through it, and what kind of help you will need. To learn more, visit Questions to Ask Your Doctor about Treatment.
The following types of treatment are used:
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the area of the body with cancer. External radiation therapy is used to treat seminoma.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (also called chemo) uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing.
Chemotherapy for extragonadal germ cell tumors is usually systemic, meaning it is injected into a vein or given by mouth. When given this way, the drugs enter the bloodstream to reach cancer cells throughout the body.
Chemotherapy drugs used to treat extragonadal germ cell tumors may include:
Combinations of these drugs may be used. Other chemotherapy drugs not listed here may also be used.
Learn more about how chemotherapy works, how it is given, common side effects, and more at Chemotherapy to Treat Cancer and Chemotherapy and You: Support for People With Cancer.
Surgery
If you have benign tumors or tumor remaining after chemotherapy or radiation therapy, surgery may be needed.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
For some people, joining a clinical trial may be an option. There are different types of clinical trials for people with cancer. For example, a treatment trial tests new treatments or new ways of using current treatments. Supportive care and palliative care trials look at ways to improve quality of life, especially for those who have side effects from cancer and its treatment.
You can use the clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials accepting participants. The search allows you to filter trials based on the type of cancer, your age, and where the trials are being done. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Learn more about clinical trials, including how to find and join one, at Clinical Trials Information for Patients and Caregivers.
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant
High doses of chemotherapy are given to kill cancer cells. Healthy cells, including blood-forming cells, are also destroyed by the cancer treatment. Stem cell transplant is a treatment to replace the blood-forming cells. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient or a donor and are frozen and stored. After the patient completes chemotherapy, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
Treatment for extragonadal germ cell tumors may cause side effects.
For information about side effects caused by treatment for cancer, visit our Side Effects page.
Follow-up care may be needed.
As you go through treatment, you will have follow-up tests or check-ups. Some tests that were done to diagnose or stage the cancer may be repeated to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back).
After initial treatment for extragonadal germ cell tumors, your blood levels of AFP and other tumor markers will continue to be checked to find out how well the treatment is working.
Treatment of Benign Teratoma
Treatment of benign teratomas is surgery.
Learn more about this treatment in the Treatment Option Overview.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Seminoma
Treatment of seminoma extragonadal germ cell tumors may include:
- Radiation therapy for small tumors in one area, followed by watchful waiting if there is tumor remaining after treatment.
- Chemotherapy for larger tumors or tumors that have spread. If a tumor smaller than 3 centimeters remains after chemotherapy, watchful waiting follows. If a larger tumor remains after treatment, surgery or watchful waiting follow.
Learn more about these treatments in the Treatment Option Overview.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Nonseminoma
Treatment of nonseminoma extragonadal germ cell tumors may include:
- Combination chemotherapy followed by surgery to remove any remaining tumor.
Learn more about these treatments in the Treatment Option Overview.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Recurrent or Refractory Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
Treatment of extragonadal germ cell tumors that are recurrent (come back after being treated) or refractory (do not get better during treatment) may include:
Learn more about these treatments in the Treatment Option Overview.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
To Learn More About Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about extragonadal germ cell tumors, visit the Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumor Home Page.
For general cancer information and other resources from the National Cancer Institute, visit:
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government’s center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of extragonadal germ cell tumors. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/extragonadal-germ-cell/patient/extragonadal-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389213]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s E-mail Us.