Treatment - Cancer Currents Blog
Cancer treatment related news, with context from leading experts. Includes articles on new therapies, treatment side effects, and important trends in treatment-related research.
-
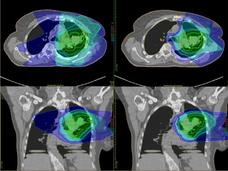
Is Proton Therapy Safer than Traditional Radiation?
Some experts believe that proton therapy is safer than traditional radiation, but research has been limited. A new observational study compared the safety and effectiveness of proton therapy and traditional radiation in adults with advanced cancer.
-
Avapritinib Approved to Treat GIST with a Rare Gene Alteration
Avapritinib (Ayvakit) has been approved for adults with gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) whose tumors have an alteration in a portion of the PDGFRA gene called exon 18. The approval applies to those whose tumors cannot be removed with surgery or have spread.
-
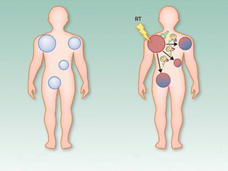
Off Target: Investigating the Abscopal Effect as a Treatment for Cancer
In people with cancer, the abscopal effect occurs when radiation—or another type of localized therapy—shrinks a targeted tumor but also causes untreated tumors in the body to shrink. Researchers are trying to better understand this phenomenon and take advantage of it to improve cancer therapy.
-
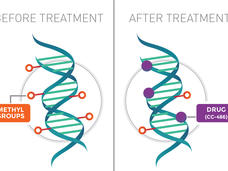
Maintenance Therapy with CC-486 Extends Survival of Adults with AML
Maintenance therapy with CC-486 extended overall survival of adults with the blood cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a large clinical trial. CC-486 is a pill form of another cancer therapy called azacitidine (Vidaza).
-
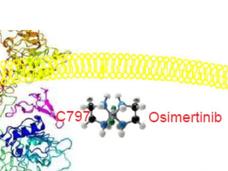
Osimertinib Improves Survival in Advanced Lung Cancer with EGFR Mutations
Osimertinib (Tagrisso) improves survival in people with non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR mutations, updated clinical trial results show. People treated with osimertinib lived longer than those treated with earlier-generation EGFR-targeted drugs.
-
Surgery for Recurrent Ovarian Cancer Does Not Improve Survival
Secondary surgery for women with recurrent ovarian cancer does not improve how long those women live, findings from a large trial show. The results call into question the current standard of practice for these patients.
-
Gilteritinib Improves Survival in AML with FLT3 Mutations
People with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with FLT3 gene mutations treated with gilteritinib had improved survival, higher rates of remission, and fewer side effects than those treated with chemotherapy, a recent trial found.
-
Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Can Skip Radiation to the Brain
Only 1.5% of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who skipped radiation had a recurrence in the central nervous system, according to a recent trial. The therapy, which is intended to prevent such a recurrence, can have devastating side effects.
-
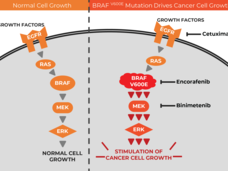
Targeted Drug Trio Improves Survival in Colorectal Cancer with BRAF Mutations
For people with colorectal cancer with a specific mutation in the BRAF gene, a treatment regimen of three targeted drugs can improve how long they live without increasing their risk of serious side effects, results from a new clinical trial show.
-
Durvalumab Plus Chemotherapy Improves Survival in Small Cell Lung Cancer
A large clinical trial showed that adding the immunotherapy drug durvalumab (Imfinzi) to standard chemotherapy can prolong survival in some people with previously untreated advanced small cell lung cancer.
-
PARP Inhibitors Show Promise as Initial Treatment for Ovarian Cancer
In three large clinical trials of women with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer, treatment with a PARP inhibitor as first-line therapy, maintenance therapy, or both, extended the length of time before participants’ cancers came back or got worse.
-
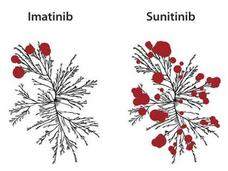
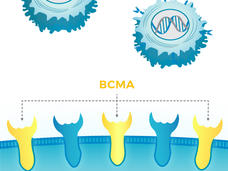
Failed Alzheimer’s Drug Might Boost CAR T-Cell Therapy for Multiple Myeloma
Results from a new study suggest a potential way to improve the effectiveness of CAR T-cell therapy for multiple myeloma. The approach relies on a class of drugs called gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSIs), several of which have been studied to treat Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Analysis Shows Women with High Breast Cancer Recurrence Scores Benefit from Chemo
A TAILORx analysis shows women with early-stage breast cancer and high recurrence scores on the Oncotype DX who received chemotherapy with hormone therapy had better long-term outcomes than what would be expected from hormone therapy alone.
-
Dual-Function Virus Engineered to Kill Tumor Cells and Support Immune Cells
Researchers have engineered an oncolytic virus to kill cancer cells and boost the immune response against tumors. In a new study, the virus provided T cells around tumors with a hormone they need for their own cell-killing functions.
-
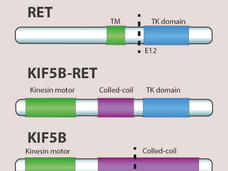
Selpercatinib Shows Promise against Lung Cancers with Alterations in RET Gene
The investigational drug selpercatinib may benefit patients with lung cancer whose tumors have alterations in the RET gene, including fusions with other genes, according to results from a small clinical trial.
-
For Children with Neuroblastoma, Trial Results Highlight Continued Evolution of Treatment
For many children with high-risk neuroblastoma, receiving two separate stem cell transplants is more beneficial than receiving one, according to the results of an NCI-supported clinical trial conducted by the Children’s Oncology Group.
-
FDA Approves Entrectinib Based on Tumor Genetics Rather Than Cancer Type
FDA has approved entrectinib (Rozlytrek) for the treatment of children and adults with tumors bearing an NTRK gene fusion. The approval also covers adults with non-small cell lung cancer harboring a ROS1 gene fusion.
-
For Some Women with Breast Cancer, Cost Influences Decisions about Surgery
In a survey of nearly 600 breast cancer survivors, researchers found that the cost of care factored into the decisions the women made about what type of surgery to get. Many women also reported never discussing costs with their physicians.
-
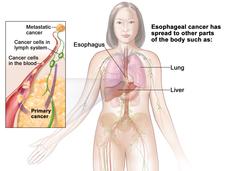
Pembrolizumab Approved for Some Patients with Advanced Esophageal Cancer
FDA has approved the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to treat some patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Patients must have certain levels of the protein PD-L1 on their tumors, as determined by an FDA-approved test.
-
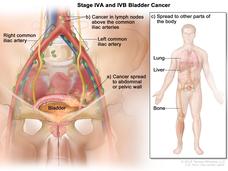
Targeted Drug Erdafitinib Benefits Some Patients with Advanced Bladder Cancer
New clinical trial findings confirm that the targeted therapy erdafitinib (Balversa) can benefit patients with advanced bladder cancer whose tumors have a genetic alteration in one of the four FGFR genes.