Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute. Learn more about Cancer Currents.
-
As Rates of Some Cancers Increase in Younger People, Researchers Search for Answers
As diagnoses of colorectal, breast, and other cancers continue to climb in people under age 50, researchers are trying to understand what’s behind this phenomenon. Is it environmental exposures, genetics, lifestyle? The culprits, they say, remain unclear.
-
Rapid Genetic Test Could Help Guide Brain Cancer Surgery
Scientists have developed a test for use during brain cancer surgery that rapidly measures the levels of certain genetic mutations in patients’ tumor samples. The test uses droplet digital polymerase chain reaction technology and produces results within 15 minutes.
-
Will This Cancer Metastasize? Check Its “Stickiness”
A device that measures the “stickiness” of cancer cells in tumor samples may help predict the likelihood of a patient’s cancer metastasizing. Researchers believe the device could eventually help doctors make more informed treatment choices.
-
FDA Approval Likely to Change Initial Treatment for Some People with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
FDA has approved the combination of the immunotherapy drugs ipilimumab (Yervoy) and nivolumab (Opdivo) for the initial treatment of people with advanced colorectal cancer whose tumors are classified as MSI-H or dMMR.
-
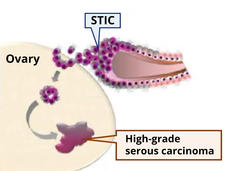
What’s at the Root of Ovarian Cancer? New Study May Have Found Part of the Answer
A subgroup of mesenchymal stem cells, called high-risk MSCs, appears to fuel the formation of cancerous lesions in the fallopian tubes and the lesions’ transition to ovarian cancer, a study has found.
-
Are New Immune-Based Treatments for Kidney and Pancreatic Cancer on the Horizon?
In small trials, personalized treatment vaccines appeared to prevent cancer from returning in patients who had successful surgery to remove their tumors. The treatments, which were created based on intensive analyses of patients’ tumors, appeared to be safe.
-
For AYAs with Advanced Cancer, Study Finds Serious Communication Gaps About Their Care
Documented conversations on goals of care are uncommon in AYA patients with advanced cancer. Researchers found that many patients did not have these discussions until the last month of life, and many asked about palliative care.
-
Expanding Research on Dormant Cancer Cells Aims to Prevent Metastasis
Some cancers come back many years after successful treatment, often as metastatic disease. Researchers believe if and how this happens is heavily influenced by dormant cancer cells and their interaction with the immune system.
-
Experimental Treatment Uses Engineered Fat Cells to “Starve” Tumors
Researchers have developed a form of cancer treatment that uses fat cells engineered to aggressively consume nutrients like glucose. When implanted in mice, the engineered cells appeared to outcompete tumors for nutrients, shrinking tumors.
-
Zenocutuzumab Approved to Treat Lung and Pancreatic Cancers with Rare Genetic Change
FDA has approved zenocutuzumab (Bizengri) to treat people with pancreatic or non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have a rare genetic alteration called an NRG1 fusion. The approval is based on a clinical trial in which the drug shrank tumors in a third of patients.
-
Intensive Program Helps People Being Screened for Lung Cancer Quit Smoking
Results from a large NCI-funded clinical trial show that a comprehensive program that integrates intensive counseling and cessation medications may be a particularly effective way to help smokers being screened for lung cancer quit.
-
Combination Therapy for Metastatic Prostate Cancer Helps Some Men Live Longer
For men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, initial treatment with enzalutamide (Xtandi) combined with talazoparib (Talzenna) may help them live longer than getting enzalutamide alone, according to updated results from a large clinical trial.
-
TACE-Based Treatment Combinations Effective Against Intermediate-Stage Liver Cancer
Results from two clinical trials show that combining a procedure called TACE with an immunotherapy drug and angiogenesis inhibitor improves how long people with intermediate-stage liver cancer live without their disease returning or getting worse.
-
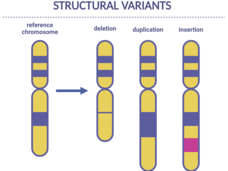
Scientists Find Genetic Changes Linked to Cancer in Children
Certain inherited genetic changes are likely involved in the development of some cancers in children, a new study shows. The changes, called structural variants, were linked with a small percentage of children with neuroblastoma, Ewing sarcoma, and osteosarcoma.
-
Can AI Help Predict Which Cancer Patients Should Be Treated with Immunotherapy?
An AI-based tool called SCORPIO more accurately predicted whether cancer patients’ tumors would respond to checkpoint inhibitors than currently available tests, a new study found. It also predicted how long patients would live after treatment.
-
Abnormal Results from Prenatal Blood Test Could Point to Cancer in the Mother
Unusual results from prenatal testing can indicate that the mother has cancer, a new study has found. The study also suggests that whole-body imaging as part of the follow-up on abnormal results can accurately identify these cancers.
-
FDA Approves Injectable Nivolumab, an Alternative to IV Infusion
The injectable form of nivolumab, called Opdivo Qvantig, is quicker and easier to give, several oncologists said, and is just as effective as the intravenous form. Injectable forms of other immunotherapies are also on the horizon.
-
Many Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Are Not Getting the Recommended Treatments, Study Finds
Many U.S. doctors aren’t using the recommended initial treatments for their patients with hormone-sensitive metastatic prostate cancer, a new study has found. Often, it’s because they aren’t up to date on the latest treatment recommendations or because of side effect concerns.
-
Blinatumomab Boosts Chemotherapy as Initial Treatment for Some Kids with ALL
Following positive results from a clinical trial, the immunotherapy drug blinatumomab (Blincyto) is expected to become part of the standard initial treatment for many kids with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the most common form of childhood cancer.
-
Study Aims to Reduce Lung Cancer Stigma by Teaching Health Professionals Empathy
Researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center have developed a training program to help health providers reduce lung cancer stigma. In this interview, they discuss an ongoing NCI-funded nationwide clinical trial to test the training.