Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute. Learn more about Cancer Currents.
-
Catch-Up HPV Testing May Help Prevent Cervical Cancer in Some Over Age 65
It may be worthwhile for some individuals between ages 65 and 69 to get tested for HPV, findings from a Danish study suggest. Specifically, the testing may help prevent cervical cancer among those who haven’t had cervical cancer screening for at least 5 years.
-
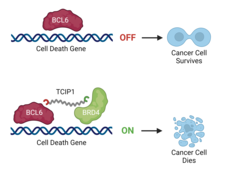
New Class of Compounds Rewires Cancer Cells to Self-Destruct
Researchers have created a molecule that, in cancer cells, hooks onto the protein BCL6 at one end and another protein that turns genes on at the other end. The result: self-destruct genes are turned up, causing the cancer cells to die.
-
Engaging People with Low-Grade Glioma in Cancer Research
An NCI-supported study called OPTIMUM, part of the Cancer Moonshot, was launched to improve the care of people with brain tumors called low-grade glioma in part by bringing them into glioma-related research.
-
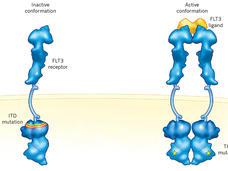
Quizartinib Approval Adds New Treatment Option for AML, Including in Older Patients
Treatment options for people with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have expanded yet again. On July 20, FDA approved quizartinib (Vanflyta) combined with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for AML with a specific change in the FLT3 gene.
-
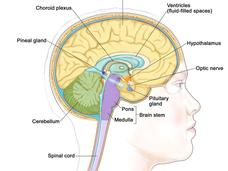
Targeted Drug Combo May Change Care for Rare Brain Tumor Craniopharyngioma
Treating craniopharyngioma often requires surgery, radiation therapy, or both. But results of a study suggest that, for many, combining the targeted therapies vemurafenib (Zelboraf) and cobimetinib (Cotellic) may substantially delay, or even eliminate, the need for these treatments.
-
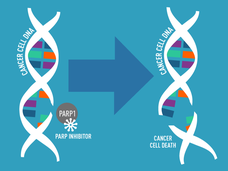
FDA Approves New Initial Treatment Option for Some Metastatic Prostate Cancers
FDA approved enzalutamide (Xtandi) combined with talazoparib (Talzenna) for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with alterations in any of 12 DNA repair genes. The drug combination, which blocks both DNA repair activities and hormones that fuel cancer growth, was more effective than the standard treatment in a large clinical trial.
-
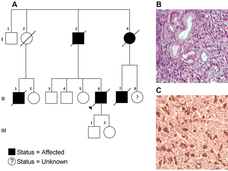
Few People with Cancer Undergo Testing for Inherited Gene Mutations
Despite recommendations, a new analysis shows few people with cancer undergo germline testing to learn if their cancer may have been caused by gene changes inherited from a parent. Germline testing can help doctors determine the best treatments for a patient and help identify people whose family members may be at higher risk of cancer.
-
Loss of Y Chromosome in Men Makes Bladder Cancer More Aggressive
In men, loss of the Y chromosome in bladder cancer cells helped tumors evade the immune system and grow unchecked, a new study shows. However, losing the chromosome also appears to make bladder cancer more susceptible to immunotherapy, researchers reported.
-
New on NCI’s Website for July 2023 – Researcher/Trainee Special Edition
An update on new and updated content on NCI’s websites of interest to the cancer community. This edition features resources of interest to cancer researchers and trainees.
-
Some People with Rectal Cancer Can Skip Radiation before Surgery
Radiation may not be needed for people undergoing surgery for rectal cancer, a large clinical trial has shown. A combination of two chemotherapy drugs before surgery appears to be as effective as chemo and radiation and may spare patients from long-term side effects.
-
Three-Drug Regimen Improves Protection against GVHD after Stem Cell Transplant
A large clinical trial has shown that in people with blood cancers, a cyclophosphamide-based regimen better protects against graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD) after an allogeneic stem cell transplant than the standard regimen.
-
Trial Confirms CAR T-Cell Therapy Benefits People with Aggressive Lymphomas
New findings show that the CAR T-cell therapy axicabtagene ciloleucel (Yescarta) improved survival for people with large B-cell lymphoma that was not responding to initial treatment or had quickly relapsed. The new results from the ZUMA-7 trial offer real hope for this group of patients.
-
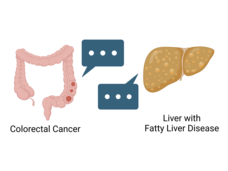
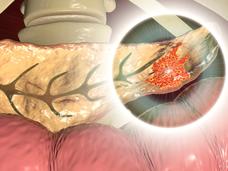
How Fatty Liver Disease Helps Cancer Thrive in the Liver
When colorectal cancer spreads to the liver, it can be very difficult to treat. Cancer is more likely to invade the liver when patients have fatty liver disease. A recent study places the blame on “message bubbles” called extracellular vesicles that are released by the liver.
-
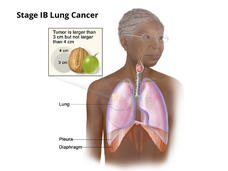
Lung Cancer Trial of Osimertinib Draws Praise—and Some Criticism
In the ADAURA clinical trial, people with early-stage lung cancer treated with osimertinib (Tagrisso) after surgery lived longer than people treated with a placebo after surgery. Despite some criticisms about its design, the trial is expected to change patient care.
-
Vorasidenib Treatment Shows Promise for Some Low-Grade Gliomas
In a large clinical trial, vorasidenib slowed the growth of low-grade gliomas that had mutations in the IDH1 or IDH2 genes. Vorasidenib is the first targeted drug developed specifically to treat brain tumors.
-
No Glucose? Pancreatic Cancer May Have a Ready Energy Alternative
A new study finds that pancreatic cancer cells have a ready way to overcome a lack of glucose, a frequent occurrence in this disease. They use another fuel source: a molecule called uridine. Findings from a related study suggest other cancers do as well.
-
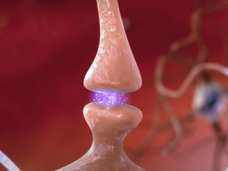
How Some Brain Tumors Hijack the Mind to Grow
Researchers have found that the aggressive brain cancer glioblastoma can co-opt the formation of new synapses to fuel its own growth. This neural redirection also appears to play a role in the devastating cognitive decline seen in many people with glioblastoma.
-
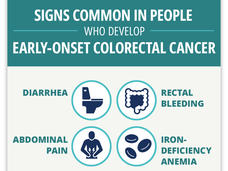
Study Identifies Potential Warning Signs of Colorectal Cancer in Younger Adults
Researchers have identified four warning signs that they believe may help identify colorectal cancer early in younger adults. The signs or symptoms are abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, and iron deficiency anemia.
-
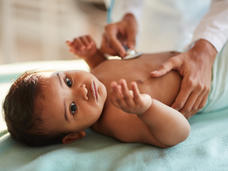
Blinatumomab Increases Survival for Infants with an Aggressive Type of ALL
Giving the drug blinatumomab (Blincyto) after standard chemotherapy substantially increased survival for infants with an aggressive form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a recent study showed. If confirmed in larger studies, the treatment may become standard therapy for infants with ALL caused by KMT2A rearrangements.
-
Can Cancer Prevention Be Better Integrated into Primary Care?
When it comes to cancer prevention, primary care clinicians play a critical role. But there are many barriers to integrating cancer prevention into primary care. Researchers are trying to better understand those barriers and how best to overcome them.