Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute. Learn more about Cancer Currents.
-
Alcohol Tied to 750,000 Cancer Cases Worldwide in 2020
Nearly 750,000 cases of cancer diagnosed worldwide in 2020, or 4%, can be attributed to alcohol consumption, according to a new study. While heavy drinking accounted for most cases, light and moderate drinking accounted for a modest amount.
-
New Task Force Focuses on Quality of Life for AYAs with Cancer
Cancer can greatly disrupt life for adolescents and young adults, who are already going through major life changes. Gathering data on how cancer and its treatment affect this age group will improve their quality of life during and beyond treatment.
-
FDA Approval of Rylaze Will Address Drug Shortage for Childhood ALL
FDA has approved a new form of asparaginase called Rylaze. The drug was developed to help alleviate shortages of Erwinia asparaginase, a key part of treatment for children and adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
-
Can an Antibiotic Treat Cancers that Become Resistant to PARP Inhibitors?
In lab studies, the antibiotic novobiocin showed promise as a treatment for cancers that have become resistant to PARP inhibitors. The drug, which inhibits a protein called DNA polymerase theta, will be tested in NCI-supported clinical trials.
-
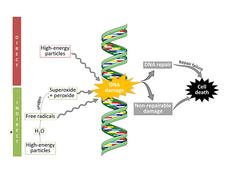
Pattern of DNA Damage Links Colorectal Cancer and Diet High in Red Meat
Researchers have discovered a consistent pattern of DNA damage in colorectal tumors that may explain how a diet high in red and processed meat can help cause colorectal cancer.
-
Advancing Cancer Prevention: A Conversation with NCI’s Dr. Philip Castle
The director of NCI’s Division of Cancer Prevention, Dr. Philip Castle, discusses the division’s priority areas and his vision for making more rapid progress in cancer prevention, including moving toward precision prevention and immunoprevention.
-
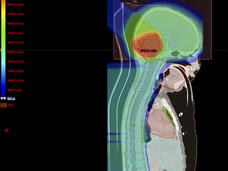
For Kids with Medulloblastoma, Trial Suggests Radiation Can Be Tailored
Standard radiation for medulloblastoma can cause long-term damage to a child’s developing brain. A new clinical trial suggests that the volume and dose of radiation could be safely tailored based on genetic features in the patient’s tumor.
-
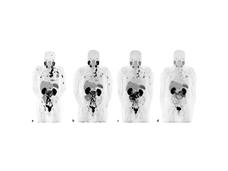
Could a Diabetes Diagnosis Help Detect Pancreatic Cancer Early?
Numerous studies have pointed to a link between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Now, several large NCI-supported studies are testing ways to pick out those people whose diabetes might be a sign of early pancreatic cancer, when treatments may be more effective.
-
For Advanced Prostate Cancer, Radiopharmaceutical Improves Survival
A drug called Lu177-PSMA-617 may be a new option for treating advanced prostate cancer. In a large clinical trial, adding the drug—a type of radiopharmaceutical—to standard treatments improved how long participants lived.
-
FDA Approval of KRAS Inhibitor Sotorasib for Lung Cancer Hailed as Milestone
FDA has approved the first KRAS-blocking drug, sotorasib (Lumakras). The approval, which covers the use of sotorasib to treat some patients with advanced lung cancer, sets the stage for other KRAS inhibitors already in development, researchers said.
-
Avasopasem Shields Normal Cells from Radiation, Helps Kill Cancer Cells
A drug called avasopasem manganese, which has been found to protect normal tissues from radiation therapy, can also make cancer cells more vulnerable to radiation treatment, a new study in mice suggests.
-
Nivolumab and Relatlimab Combination Shows Promise in Advanced Melanoma
People with advanced melanoma treated with two immunotherapy drugs—nivolumab (Opdivo) and a new drug called relatlimab—lived longer without their cancer getting worse than those treated only with nivolumab, results from a large clinical trial show.
-
Nivolumab-Based Combinations Improve Survival in Advanced Esophageal Cancer
A treatment regimen that combines the immunotherapy drug nivolumab (Opdivo) with either another immunotherapy drug or chemotherapy may be a new initial treatment option for people with advanced esophageal cancer, a large clinical trial finds.
-
Should People Over Age 75 Be Screened for Colorectal Cancer?
Screening people for colorectal cancer after age 75 may be beneficial, a new study suggests. The findings provide helpful information for physicians to use in discussing screening choices with their older patients.
-
For Hairy Cell Leukemia, Drug Combination Leads to Long-Lasting Remissions
In a small study, vemurafenib (Zelboraf) and rituximab (Rituxan) helped 85% of participants stay in remission for nearly 3 years. The study involved 30 people with hairy cell leukemia that had come back after or had not responded to previous treatment.
-
COVID-19 Vaccines May Be Less Effective in Some People with Cancer
People with blood cancers seem to be less protected by COVID-19 vaccines than those with other cancers and people without cancer, three new studies suggest. Experts believe this limited effectiveness is likely due to patients’ weakened immune systems.
-
For Early-Stage Cervical Cancer, Minimally Invasive Surgery Declining
Fewer women with early-stage cervical cancer are having minimally invasive surgery, including robotic, as part of their treatment, a new study shows. The shift toward more open surgeries follows the release of results from the LACC trial in 2018.
-
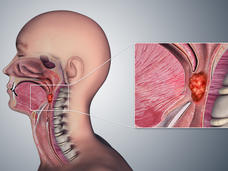
Treatments for Oropharyngeal Cancer Are Very Effective, But Are There Ways to Do Less Harm?
Can some people with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, a type of head and neck cancer, get less intense treatment without risking their cancer coming back? Researchers are trying to find out.
-
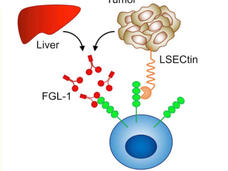
Discovery of Tumor Suppressor Suggests New Cancer Treatment Strategies
Researchers have shown that the loss of a protein called AMBRA1 can cause tumors to form in mice and is linked with worse outcomes in some human tumors. The new research may lead to strategies for re-sensitizing cancer cells to CDK4/6 inhibitor drugs.
-
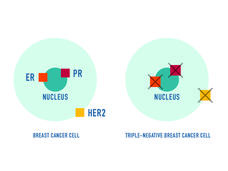
Sacituzumab Govitecan Earns Full Approval for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Sacituzumab govitecan (Trodelvy) now has regular FDA approval for people with locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The update follows last year’s accelerated approval of the drug for people with TNBC.