July 2021 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
FDA Approval of Rylaze Will Address Drug Shortage for Childhood ALL
FDA has approved a new form of asparaginase called Rylaze. The drug was developed to help alleviate shortages of Erwinia asparaginase, a key part of treatment for children and adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
-
Can an Antibiotic Treat Cancers that Become Resistant to PARP Inhibitors?
In lab studies, the antibiotic novobiocin showed promise as a treatment for cancers that have become resistant to PARP inhibitors. The drug, which inhibits a protein called DNA polymerase theta, will be tested in NCI-supported clinical trials.
-
Pattern of DNA Damage Links Colorectal Cancer and Diet High in Red Meat
Researchers have discovered a consistent pattern of DNA damage in colorectal tumors that may explain how a diet high in red and processed meat can help cause colorectal cancer.
-
Advancing Cancer Prevention: A Conversation with NCI’s Dr. Philip Castle
The director of NCI’s Division of Cancer Prevention, Dr. Philip Castle, discusses the division’s priority areas and his vision for making more rapid progress in cancer prevention, including moving toward precision prevention and immunoprevention.
-
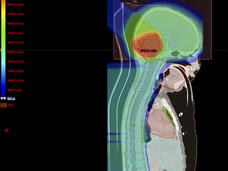
For Kids with Medulloblastoma, Trial Suggests Radiation Can Be Tailored
Standard radiation for medulloblastoma can cause long-term damage to a child’s developing brain. A new clinical trial suggests that the volume and dose of radiation could be safely tailored based on genetic features in the patient’s tumor.
-
Could a Diabetes Diagnosis Help Detect Pancreatic Cancer Early?
Numerous studies have pointed to a link between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Now, several large NCI-supported studies are testing ways to pick out those people whose diabetes might be a sign of early pancreatic cancer, when treatments may be more effective.