June 2020 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
Responding to Coronavirus, Cancer Researchers Reimagine Clinical Trials
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, cancer researchers are making changes to clinical trials to ensure patient safety and protect the integrity of their work. Some changes, such as greater use of telemedicine, will likely continue into the future.
-
Study Clarifies Timing of Immunotherapy for Advanced Bladder Cancer
Results from a large study show that, for most people with advanced bladder cancer, starting immunotherapy with avelumab (Bavencio) shortly after initial treatment with chemotherapy is better than delaying treatment.
-
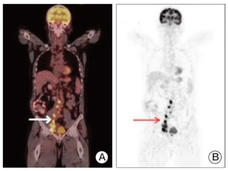
Selpercatinib Approved for Thyroid and Lung Cancers with RET Gene Alterations
FDA has granted accelerated approval for selpercatinib (Retevmo) to treat certain patients with thyroid cancer or non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have RET gene alterations. The drug, which works by blocking the activity of RET proteins, was approved based on the results of the LIBRETTO-001 trial.
-
Olanzapine Reduces Nausea and Vomiting Caused by Advanced Cancer
Many advanced cancer patients suffer from chronic nausea and vomiting and there aren’t many good treatments available. But a small study suggests that the drug olanzapine (Zyprexa) may fill that gap.
-
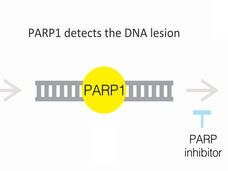
With Two FDA Approvals, Prostate Cancer Treatment Enters the PARP Era
FDA has approved olaparib (Lynparza) and rucaparib (Rubraca) to treat some men with metastatic prostate cancer. The PARP inhibitors are approved for men whose cancers have stopped responding to hormone treatment and have specific genetic alterations.
-
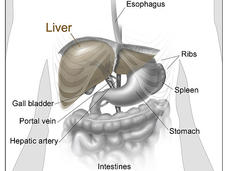
Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Approved to Treat Liver Cancer
FDA has approved atezolizumab (Tecentriq) plus bevacizumab (Avastin) as an initial treatment for some people with advanced liver cancer. This is the first approval in 13 years for a treatment that is more effective than the current standard, sorafenib.
-
Study Examines Whether Blood Test Can Identify Early Cancers
A blood test combined with imaging tests detected tumors—some at an early stage—in women with no history of cancer or symptoms, a recent study showed. The test also mistakenly indicated some women had cancer when further testing showed they didn't.