May 2021 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
COVID-19 Vaccines May Be Less Effective in Some People with Cancer
People with blood cancers seem to be less protected by COVID-19 vaccines than those with other cancers and people without cancer, three new studies suggest. Experts believe this limited effectiveness is likely due to patients’ weakened immune systems.
-
For Early-Stage Cervical Cancer, Minimally Invasive Surgery Declining
Fewer women with early-stage cervical cancer are having minimally invasive surgery, including robotic, as part of their treatment, a new study shows. The shift toward more open surgeries follows the release of results from the LACC trial in 2018.
-
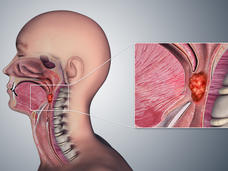
Treatments for Oropharyngeal Cancer Are Very Effective, But Are There Ways to Do Less Harm?
Can some people with HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer, a type of head and neck cancer, get less intense treatment without risking their cancer coming back? Researchers are trying to find out.
-
Discovery of Tumor Suppressor Suggests New Cancer Treatment Strategies
Researchers have shown that the loss of a protein called AMBRA1 can cause tumors to form in mice and is linked with worse outcomes in some human tumors. The new research may lead to strategies for re-sensitizing cancer cells to CDK4/6 inhibitor drugs.
-
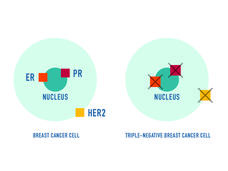
Sacituzumab Govitecan Earns Full Approval for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Sacituzumab govitecan (Trodelvy) now has regular FDA approval for people with locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). The update follows last year’s accelerated approval of the drug for people with TNBC.
-
Brentuximab May Mean Less Radiation for Children, Teens with Hodgkin Lymphoma
In a recent study, a treatment regimen using brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) instead of the chemotherapy drug vincristine allowed some children and teens with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma to avoid radiation therapy—and the long-term health problems that can come with it.
-
Topotecan–Berzosertib Combination Shows Promise against Small Cell Lung Cancer
Combining the chemotherapy drug topotecan and the investigational drug berzosertib shrank tumors in some patients with small cell lung cancer, results from an NCI-supported phase 1 clinical trial show. Two phase 2 trials of the combination are planned.