Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute.
-
3-in-1 Approach Helps Women in Rural Areas Get Cancer Screenings
In a new study, providing rural women with an interactive video about cancer screening and follow-up calls with patient navigators helped get them up to date on screenings for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer.
-
Drug Regimen Boosts Survival of People with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
A new treatment regimen may help improve the survival of some people with advanced colorectal cancer, according to results from an international clinical trial. The new regimen includes bevacizumab (Avastin) and the combination of trifluridine and tipiracil (Lonsurf).
-
Motixafortide May Improve Stem Cell Transplants for People with Multiple Myeloma
In a clinical trial of people with multiple myeloma, giving motixafortide with filgrastim markedly increased the number of stem cells that could be collected. The treatment may allow more people with this cancer to get optimal numbers of stem cells for a transplant.
-
When Prenatal DNA Tests Point to Cancer
An NIH-led study called IDENTIFY is analyzing what happens when prenatal blood tests in a pregnant person suggests the person may have cancer. Dr. Diana Bianchi and Amy Turriff talk about their experience with the study thus far.
-
Can the New “Omics” on the Block Find Liver Cancer in Blood?
Researchers have developed a blood test that, in a preliminary study, accurately detected liver cancer, including in people with early-stage disease. The test uses a new type of technology called fragmentomics to analyze bits of DNA in the blood.
-
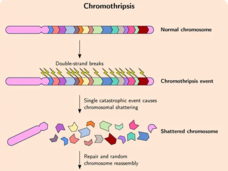
Coming Full Circle on Cancer and Extrachromosomal DNA
A new study shows for the first time that a circular form of DNA, called ecDNA, is present in precancerous tissue and not just cancer cells. The study also suggested that when ecDNA is present in Barrett’s esophagus, that tissue is almost certain to become cancer.
-
Rare Melanoma Very Likely to Respond to Treatment with Pembrolizumab
People with desmoplastic melanoma, a rare form of skin cancer, are likely to benefit from treatment with a single immunotherapy drug, pembrolizumab (Keytruda), according to new results from a small clinical trial.
-
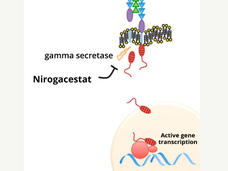
Nirogacestat May Offer Hope to People with Desmoid Tumors
In a clinical trial, the drug nirogacestat shrank tumors in 40% of people with desmoid tumors. Treatment with nirogacestat also substantially improved progression-free survival, pain, and physical functioning, compared with patients treated with a placebo.
-
Multiple mRNA Vaccines Show Promise for Treating HPV-Related Cancers
A new study has compared three formulations of an mRNA vaccine designed to treat cancers caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. All three vaccines showed promise in mice.
-
Financial Navigation Can Reduce the Financial Toxicity of Cancer Care
The high cost of cancer care can cause added distress and life disruptions for patients as well as their loved ones. Researchers at the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center found that a financial navigation program saved patients and their loved ones an average of about $2,500 each.
-
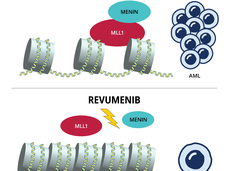
Revumenib Shows Promise in Treating Advanced Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Treatment with revumenib caused complete remission in about one-third of participants in an early-phase clinical trial involving patients who’d had many prior treatments. Revumenib is part of a new class of targeted drugs known as menin inhibitors.
-
Transforming Cancer Clinical Trials for Better, Faster Results
In this Q&A, NCI Director Dr. Monica Bertagnolli and Deputy Director for Clinical and Translational Research Dr. James Doroshow explain the challenges of cancer clinical trials and important steps NCI is taking to improve their effectiveness.
-
Immunotherapy’s Role in Treating Endometrial Cancer Expected to Grow
In two clinical trials, combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with standard chemotherapy substantially increased how long people with advanced endometrial cancer lived without their cancer worsening, particularly those with dMMR or MSI-high tumors.
-
Liquid Biopsies on the Horizon for Children with Solid Cancers
Results from a new study highlight the progress being made toward developing liquid biopsies specifically for use in children with solid cancers like Ewing sarcoma and Wilms tumor. The tests can help detect and diagnose cancer and monitor for response to treatment and recurrence.
-
Cancer and Climate Change: The Health Threats of Unnatural Disasters
The consequences of climate change have already affected cancer care in the United States, particularly in areas hit by hurricanes and wildfires. Researchers are studying how to mitigate that impact and better understand the effect of climate change on the risk of developing cancer.
-
Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research: A Unique Resource for the Biomedical Research Community
To mark the 10 years since it was named a national lab, NCI Principal Deputy Director Douglas R. Lowy, M.D., discusses some of the Frederick National Lab’s initiatives to support cancer research and looks ahead at the next 10 years.
-
Immunotherapy after Surgery Shows Long-Term Benefits for High-Risk Bladder Cancer
Updated results from a large clinical trial confirm that, for some people with bladder cancer, receiving immunotherapy after surgery is an effective treatment. In 2021, initial results from the same trial led to FDA approval of nivolumab (Opdivo) for this use.
-
Strategy May Prevent Tumor Resistance to Targeted Cancer Therapies
Researchers have identified a mechanism by which cancer cells develop specific genetic changes needed to become resistant to targeted therapies. They also showed that this process, called non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), can potentially be disrupted.
-
Dexrazoxane Protects the Heart Long Term for Kids Being Treated for Cancer
Doxorubicin is used to treat many types of childhood cancer, but it can damage the heart. Giving dexrazoxane (Zinecard) before each dose substantially decreases a child’s risk of treatment-related heart problems in adulthood, new study results show.
-
Lung-Sparing Surgery Is Effective for Some with Early-Stage Lung Cancer
For certain people with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer, sublobar surgery to remove only a piece of the affected lung lobe is as effective as surgery to remove the whole lobe, new research shows.