Clinical Trial Results - Cancer Currents Blog
Reports on findings from cancer clinical trials, with commentary from leading researchers on how the trial results will affect patient care.
-
Can Acupuncture Help Cancer Survivors with Chronic Pain?
In a large clinical trial, cancer survivors treated with acupuncture had modest improvements in chronic pain compared with those who received standard pain treatments. The study couldn’t rule out a placebo effect for the improvement with acupuncture.
-
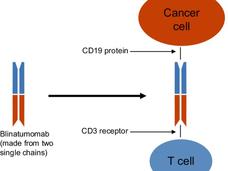
Blinatumomab Improves Survival in Children with Relapsed Leukemia
The results of two trials establish blinatumomab (Blincyto) as a new standard treatment for children and young adults with high-risk relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia after remission has been achieved and before a stem cell transplant.
-
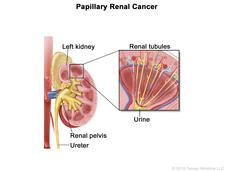
Targeted Therapy Cabozantinib Slows Progression of Rare Kidney Cancer
Cabozantinib (Cabometyx) is an effective initial treatment for people with metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC), a rare type of kidney cancer. A clinical trial showed the drug was more effective than the current standard treatment.
-
Trial Tests Abemaciclib As New Option for Early-Stage Breast Cancer
The drug abemaciclib (Verzenio) may be a new treatment option for people with the most common type of breast cancer, with new study findings suggesting that it can reduce the risk of the cancer returning.
-
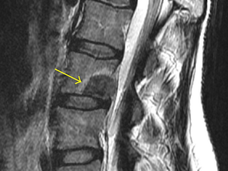
Targeted Radiation Reduces Pain from Cancer Metastases in the Spine
For some patients with painful spinal metastases from advanced cancer, a type of precise, high-dose radiation therapy—called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)—may be a highly effective way to relieve that pain, clinical trial results show.
-
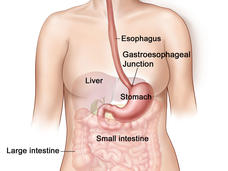
Nivolumab Improves Survival for Some Patients with Advanced Stomach Cancer
For some people with advanced stomach cancer, the drug nivolumab (Opdivo) plus chemotherapy may improve how long they live, results from a large clinical trial show. The trial also included patients with gastric cancers that involve the esophagus.
-
For Esophageal Cancer, Immunotherapy Likely to Play Larger Role
For some people with advanced esophageal cancer, the immunotherapy drugs pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and nivolumab (Opdivo) may become part of early treatment for the disease, according to results from two large clinical trials.
-
Pazopanib Shows Promise for Children, Adults with Soft Tissue Sarcomas
For children and adults with advanced soft tissue sarcoma, adding pazopanib (Votrient) to chemotherapy and radiation before surgery may be a promising treatment option, early results from a clinical trial suggest.
-
Regular Aspirin Use May Increase Older People’s Risk of Dying from Cancer
Regular use of low-dose aspirin may increase an older person’s risk of being diagnosed with advanced cancer and of dying from cancer, results from the ASPREE clinical trial suggest. Learn more about what this 19,000-participant study found.
-
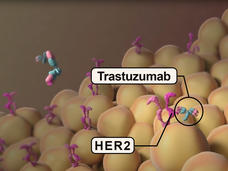
Trastuzumab May Improve Survival in Women with Rare Endometrial Cancer
For some women with HER2-positive uterine serous carcinoma, a rare type of endometrial cancer, treating them with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and chemotherapy may help them live longer, according to updated results from a small clinical trial.
-
New Drug Regimen Cures More Children with Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma
For children with aggressive Burkitt lymphoma and other B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, adding rituximab (Rituxan, Truxima) to chemotherapy substantially increases the likelihood of the child being cured, results from a large clinical trial show.
-
Responding to Coronavirus, Cancer Researchers Reimagine Clinical Trials
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, cancer researchers are making changes to clinical trials to ensure patient safety and protect the integrity of their work. Some changes, such as greater use of telemedicine, will likely continue into the future.
-
Study Clarifies Timing of Immunotherapy for Advanced Bladder Cancer
Results from a large study show that, for most people with advanced bladder cancer, starting immunotherapy with avelumab (Bavencio) shortly after initial treatment with chemotherapy is better than delaying treatment.
-
Olanzapine Reduces Nausea and Vomiting Caused by Advanced Cancer
Many advanced cancer patients suffer from chronic nausea and vomiting and there aren’t many good treatments available. But a small study suggests that the drug olanzapine (Zyprexa) may fill that gap.
-
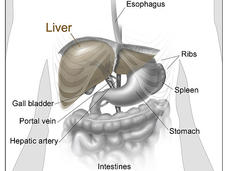
Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab Approved to Treat Liver Cancer
FDA has approved atezolizumab (Tecentriq) plus bevacizumab (Avastin) as an initial treatment for some people with advanced liver cancer. This is the first approval in 13 years for a treatment that is more effective than the current standard, sorafenib.
-
More Evidence that Ruxolitinib Benefits Some Patients with Graft-Versus-Host Disease
Patients with acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) that does not respond to steroid therapy are more likely to respond to the drug ruxolitinib (Jakafi) than other available treatments, results from a large clinical trial show.
-
Single Dose of HPV Vaccine Yields Long-Term Protection from Many Cancer-Causing Types
More than a decade after vaccination, women who had received a single dose of the HPV vaccine continued to be protected against infection with the two cancer-causing HPV types targeted by the vaccine, an NCI-funded clinical trial shows.
-
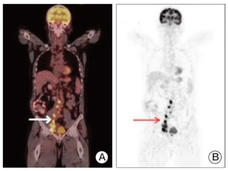
Trial Should Change Care for AIDS-Related Kaposi Sarcoma in Sub-Saharan Africa
For people with advanced AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma in sub-Saharan Africa, results from a large clinical trial are expected to change treatment. In the trial, paclitaxel greatly improved outcomes compared with treatments typically used in the region.
-
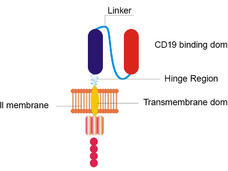
Remodeled CAR T-Cell Therapy Reduces Side Effects in First Clinical Trial
A remodeled CAR T-cell therapy causes fewer neurologic side effects and is equally effective as the original form of the treatment, according to results from the first clinical trial testing the approach in patients with B-cell lymphomas.
-
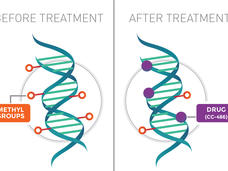
Maintenance Therapy with CC-486 Extends Survival of Adults with AML
Maintenance therapy with CC-486 extended overall survival of adults with the blood cancer acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in a large clinical trial. CC-486 is a pill form of another cancer therapy called azacitidine (Vidaza).