Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute. Learn more about Cancer Currents.
-
Stealing Strategies from Cancerous T Cells May Boost Immunotherapy
Adding a fusion of parts of two genes helped engineered T cells divide faster, kill more tumor cells, and survive longer in mice without making the T cells behave like cancer cells.
-
Nivolumab Injections Could Make Treatment Easier for More People with Cancer
In a clinical trial, an injectable form of nivolumab (Opdivo) was as effective against kidney cancer as the intravenous form of the drug. Side effects were also similar and treatment time was shorter. Injectable immunotherapies, several experts said, if found to be comparable to IV forms, can be more convenient to receive and accessible to more people.
-
First Cancer TIL Therapy Gets FDA Approval for Advanced Melanoma
In an event more than three decades in the making, FDA has approved lifileucel (Amtagvi), the first cancer treatment that uses immune cells called tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, or TILs.
-
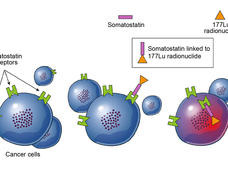
Lutathera Shows Promise as Part of Initial Therapy for Some Neuroendocrine Tumors
Adding Lu 177-dotate to the initial treatment of certain advanced neuroendocrine tumors nearly tripling the length of time people survive without their tumors getting worse, according to new clinical trial results.
-
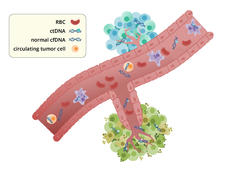
ctDNA May Guide Who Needs Chemo After Colorectal Cancer Surgery
Results from a new study suggest that the presence of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in blood samples can predict which patients with colorectal cancer should and shouldn’t get chemotherapy after surgery to remove their tumors.
-
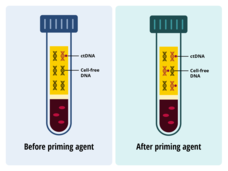
Pump Up the Volume: “Priming Agents” May Improve Cancer Liquid Biopsies
Using two different techniques, researchers showed they could temporarily boost ctDNA levels in the blood of mice with tumors. With more ctDNA in collected blood draws, a liquid biopsy could better detect cancer, the research team found.
-
Repotrectinib Expands Treatment Options for Lung Cancers with ROS1 Fusions
The results of the clinical trial that led to FDA’s 2023 approval of repotrectinib (Augtyro) for lung cancers with ROS1 fusions have been published. The drug shrank tumors in 80% of people receiving the drug as an initial treatment.
-
How a Simple Tool Is Saving Lives of Children with Cancer in Latin America
A system for catching treatment-related complications in children with cancer has proven to be highly effective in many Latin American hospitals. An NCI-funded study aims to help make these early warning systems sustainable.
-
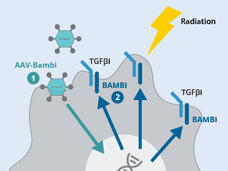
Manipulating an Immune Cell May Make Radiation Therapy More Effective, Study Suggests
In a new study in mice, researchers showed they could enhance radiation therapy by boosting levels of the BAMBI protein in MDSC immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. After radiation, T cells flooded into the tumor and killed tumors elsewhere in the body.
-
India’s First Homegrown CAR T-Cell Therapy Has Roots in NCI Collaboration
Training provided by NCI scientists helped researchers in India design an effective CAR-T cell therapy, NexCAR19, that can be manufactured in India, made available at a reasonable cost, and meet the needs of patients in India’s health care system.
-
What Happens If More People Get Screened for Cancer?
Researchers used computer modeling to estimate the number of deaths that could be prevented, and the harms caused, if more people used USPSTF-recommended cancer screening tests. The study’s lead investigator, Dr. Amy Knudsen, explains the findings.
-
Can Some People with Breast Cancer Safely Skip Lymph Node Radiation?
Some people with no evidence of cancer in nearby lymph nodes after presurgical chemotherapy can skip radiation to that area without increasing the risk of the cancer returning, a clinical trial found. But some experts caution that more details are needed.
-
Trial Results Support Adding Daratumumab to Initial Treatment for Multiple Myeloma
Adding daratumumab (Darzalex) to standard treatment helped people with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma live longer without their cancer getting worse or dying. People taking daratumumab were also more likely to have no detectable signs of cancer (minimal residual disease) after treatment.
-
For People with Inherited Risk of Stomach Cancer, Gastrectomy Has Lasting Consequences
In a recent study, more than 90% of people who’d had their stomach surgically removed to prevent cancer experienced a least one chronic complication 2 years out from their surgery. For some, the complications are life altering.
-
Enzalutamide Gets Added Approval for Prostate Cancer That Hasn’t Spread
Under a new FDA approval, enzalutamide (Xtandi) can now be used alone, or in combination with leuprolide, to treat people with nonmetastatic prostate cancer that is at high risk of returning after surgery or radiation.
-
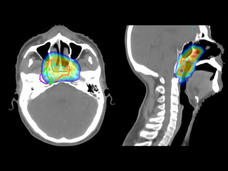
Toripalimab Becomes First Immunotherapy Drug Approved for Nasopharyngeal Cancer
FDA approved toripalimab (Loqtorzi) based on the results of a large clinical trial showing that, when added to chemotherapy, the drug extended survival in people with nasopharyngeal cancer that returned after initial treatment or spread in the body.
-
Following Abnormal Cancer Screening Results, Multi-Level Reminders May Increase Follow-Up
In a clinical trial, a simple letter and phone call helped increase the number of people who completed the recommended follow-up testing after an abnormal cancer screening result.
-
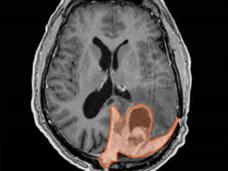
Genetic Signature May Help Tailor Treatment for Meningioma
The activity of 34 genes can accurately predict the aggressiveness of meningiomas, a new study shows. This gene expression signature may help oncologists select the best treatments for people with this common type of brain cancer than they can with current methods.
-
Virtual Mind–Body Fitness Classes Show Unexpected Benefit in People with Cancer
In a clinical trial, people being treated for cancer who participated in virtual mind–body fitness classes were less likely to be hospitalized, and had shorter stays when they were hospitalized, than people who did not take the classes.
-
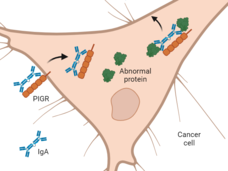
Antibody Drug Ejects Problematic Proteins from Cancer Cells
Antibodies currently used in many cancer treatments have only been able to reach proteins outside of cancer cells. In a new study in mice, scientists found a way to target cancer-fueling KRAS and IDH1 proteins buried inside cancer cells.