Treatment - Cancer Currents Blog
Cancer treatment related news, with context from leading experts. Includes articles on new therapies, treatment side effects, and important trends in treatment-related research.
-
High-Fat Diet or Diabetes Drug May Enhance Response to Targeted Cancer Drug
A study in mice may have identified a way to help overcome resistance to targeted cancer drugs known as PI3K inhibitors. The approach appears to work by reducing insulin levels in patients receiving these drugs.
-
Aggressive Prostate Cancer Subtype More Common Than Expected
Researchers have found that men with advanced prostate cancer may be more likely than previously thought to develop a more aggressive form of the disease. The subtype, called t-SCNC, was linked with shorter survival than other subtypes.
-
Developing Biomarkers for Immunotherapy: A Conversation with Drs. Magdalena Thurin and Helen Chen
NCI is supporting a new research network to develop biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy. In this interview, NCI’s Dr. Helen Chen and Magdalena Thurin explain the networks’ structure and its goals.
-
FDA Alters Approved Use of Two Checkpoint Inhibitors for Bladder Cancer
FDA has changed the approved uses of the immunotherapy drugs pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and atezolizumab (Tecentriq) to treat the most common form of bladder cancer. The change is based on whether patients’ tumors have a specific biomarker.
-
Can Age Affect Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors?
A new study has linked age with how well patients with melanoma responded to treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Experiments in mice suggested that the response pattern may be due to an age-related shift in the kinds of immune cells in tumors.
-
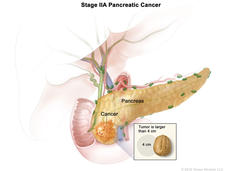
Altering Chemotherapy Improves Outcomes in Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer
Results from two clinical trials are expected to improve the outlook for some people with early-stage pancreatic cancer. Altering the chemotherapy drugs used and the timing of treatment substantially improved survival.
-
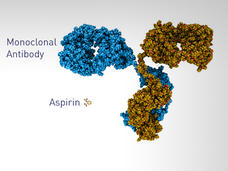
Biosimilars for Cancer Emerge as Patents on Widely Used Biological Drugs Expire
As the patents on some widely used drugs to treat cancer expire in the coming years, biosimilar drugs are being developed for the treatment of patients with cancer. Are biosimilars effective and will they expand treatment options for patients?
-
Trial Produces Practice-Changing Findings for Some Children, Young Adults with Leukemia
This NCI-funded Children’s Oncology Group trial tested the addition of nelarabine (Arranon) to standard treatment for children and young adults with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL).
-
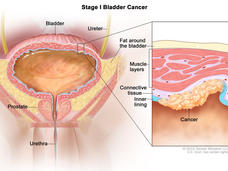
New Treatment Approach Could Help Prevent Recurrences of Some Bladder Cancers
Flushing the bladder with the chemotherapy drug gemcitabine after tumors have been removed surgically may reduce the risk of low-grade bladder cancer returning, according to the results of a large clinical trial.
-
Experimental Cancer Drug Metarrestin Targets Metastatic Tumors
Researchers have struggled to develop therapies to treat tumors that have spread to other parts of the body. In a new study, researchers tested whether the experimental drug metarrestin can selectively shrink metastases in mouse models of aggressive pancreatic cancer.
-
Can Immunotherapy Succeed in Glioblastoma?
Despite continued efforts to develop new therapies for glioblastoma, none have been able to improve how long patients live appreciably. Despite some setbacks, researchers are hopeful that immunotherapy might be able to succeed where other therapies have not.
-
Some Children with Wilms Tumor Can Receive Less Therapy, Study Suggests
Results from an NCI-sponsored clinical trial may point to an important change in how some children with advanced Wilms tumor, a form of kidney cancer, are treated.
-
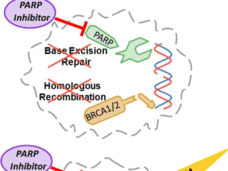
Rucaparib Approved as Maintenance Treatment for Some Recurrent Ovarian Cancers
FDA has expanded its approval of rucaparib (Rubraca) as a maintenance therapy for women with recurrent ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer whose tumors shrank after subsequent treatment with a platinum-based chemotherapy.
-
Moving Beyond BMI: Low Muscle Mass May Affect Cancer Survival
Researchers compared the risk of death for women with breast cancer who had low skeletal muscle mass, or sarcopenia, at the time of their cancer diagnosis and women who had adequate muscle mass.
-
Immunotherapy Drugs Expand Treatment Options for Advanced Lung Cancer
Results from a large clinical trial show combining an immune checkpoint inhibitor with chemotherapy helped some patients with advanced lung cancer live longer than chemotherapy alone. How will this change the lung cancer treatment landscape?
-
Take with Food: Study Tests Lowering Dose of Prostate Cancer Drug
In a small clinical trial, researchers compared the efficacy of a much lower dose of the cancer drug abiraterone (Zytiga) taken with a low-fat breakfast with a full dose taken on an empty stomach, as directed on the drug’s label.
-
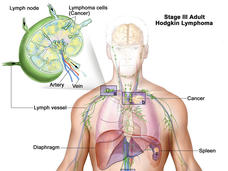
Brentuximab Approved for Initial Treatment of Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma
The FDA has expanded the approved uses of brentuximab (Adcetris) in people with Hodgkin lymphoma. Under the new approval, brentuximab can be used in combination with three other chemotherapy drugs as an initial treatment in patients with advanced disease.
-
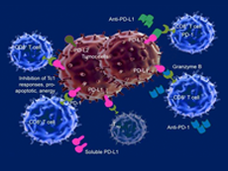
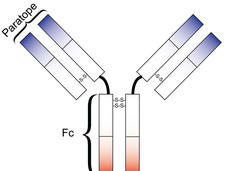
Cancer Immunotherapy Drug Simultaneously Targets Two Proteins that Block Immune Response
Two independent groups of researchers have fused a TGF-beta receptor to a monoclonal antibody that targets a checkpoint protein. The result is a single hybrid molecule called a Y-trap that blocks two pathways used by tumors to evade the immune system.
-
NCI Launches New Resource for Specimens and Data from Cancer Clinical Trials
NCI has launched Navigator, a new resource for researchers interested in using specimens and clinical data collected from large cancer clinical trials.
-
Many Men with Penile Cancer Do Not Get Recommended Treatments, Study Finds
An analysis of records from a national cancer treatment database has found that many men with penile cancer that has not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes did not undergo lymph node biopsy or receive chemotherapy, as recommended by widely used professional guidelines.