Treatment - Cancer Currents Blog
Cancer treatment related news, with context from leading experts. Includes articles on new therapies, treatment side effects, and important trends in treatment-related research.
-
Treatment for Children with Leukemia Also Effective for Adolescents, Young Adults
A clinical trial found that an intensive treatment regimen developed specifically for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia is also effective for older adolescents and young adults with the disease.
-
Dormant Tumor Cells Can Be Sensitized to Chemotherapy
A new study in mice shows that disrupting the relationship between breast cancer cells that spread to bone and normal cells surrounding them makes the cancer cells sensitive to treatment.
-
A CAR T-Cell Therapy for Multiple Childhood Cancers?
An experimental CAR T-cell therapy may have potential as a treatment for several types of childhood cancer, results from a new study in mice suggest. The CAR T cells eradicated tumors in mouse models of several different childhood cancers, including two forms of sarcoma and medulloblastoma.
-
HTAN: Mapping Tumors across Space and Time Using Cutting-Edge Technologies
The Human Tumor Atlas Network, an NCI-led collaborative research project, is creating detailed maps of cancers that will be used to learn how cancer develops, spreads, and responds to treatment.
-
Curbing Production of Immune Checkpoint Protein Slows Liver Cancer in Mice
Researchers have found an unconventional way to unleash the immune system against liver cancer in mice. The researchers used an investigational drug to curb the production of a checkpoint inhibitor protein that shields tumors from the immune system.
-
Immunotherapy Effective in Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma
People with advanced alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS), a rare cancer, appear to benefit from a type of immunotherapy called an immune checkpoint inhibitor, according to results from a small clinical trial.
-
FDA Approvals Bring New Options for Older Patients with AML
FDA has approved venetoclax (Venclexta) and glasdegib (Daurismo) for use in people with acute myeloid leukemia aged 75 and older and those with health conditions that prevent them from receiving the intensive chemotherapy regimen that is the standard initial treatment.
-
Whole- and Partial-Breast Radiation Effective at Preventing Breast Cancer from Returning
In women with early-stage breast cancer, two clinical trials have shown that both whole- and partial-breast radiation therapy are effective at preventing the cancer from returning after breast-conserving surgery.
-
Drug Combination May Target the Unique Metabolism of Leukemia Stem Cells
Two new studies show how the drugs venetoclax (Venclexta) and azacitidine (Vidaza) team up to block the unique metabolism of leukemia stem cells and may explain why the drug combination is effective against acute myeloid leukemia.
-
Targeted Treatment for Rare Digestive Tract Cancers May Extend Survival
In an early-phase trial, dabrafenib plus trametinib shrank tumors in patients with biliary tract cancer and adenocarcinoma of the small intestine whose tumors had a specific mutation in the BRAF gene.
-
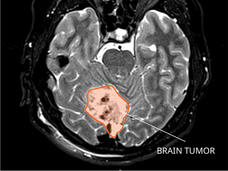
Tailored Radiation to Treat Brain Metastases Reduces Impact on Cognitive Function
Results from a clinical trial suggest that, in patients with brain metastases, an advanced radiotherapy technique limits harm to patients’ cognitive function without affecting the treatment’s effect on tumors.
-
Olaparib after Initial Treatment Delays Ovarian Cancer Progression
In a recent trial, the PARP inhibitor olaparib substantially delayed ovarian cancer from coming back after the first line of chemotherapy. Could the findings change the standard of care for newly diagnosed ovarian cancer with a BRCA mutation?
-
Immunotherapy Drug Cemiplimab Approved for Advanced Squamous Cell Skin Cancer
The Food and Drug Administration approved the immunotherapy drug cemiplimab (Libtayo) for an advanced form of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a common type of skin cancer. It is the first agent to be approved specifically for advanced SCC.
-
Trial Results Highlight Changing Lung Cancer Treatment Landscape
Results from two large clinical trials should cement the value of the drugs brigatinib (Alunbrig) and durvalumab (Imfinzi) in treating non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The trial results, several experts said, confirm that the drugs can improve the outcomes of patients with advanced NSCLC.
-
For Small Cell Lung Cancer, Immunotherapy Drug Finally Brings Improved Survival
In a large clinical trial, the immunotherapy drug atezolizumab (Tecentriq), combined with a standard chemotherapy regimen, modestly increased survival in patients with advanced small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The trial is the first in more than 20 years to show a survival improvement in this cancer.
-
Stimulating the Immune System Shrinks Some Slow-Growing Lymphomas
In a small trial involving patients with slow-growing B-cell lymphoma, injecting the compound SD-101 directly into tumors (in situ vaccination) and giving low-dose radiation shrank the injected tumors and, frequently, tumors elsewhere in the body.
-
Heart Problems: Investigating the Cardiac Side Effects of Cancer Treatments
Certain cancer treatments can damage the heart and the cardiovascular system, a problem known as cardiotoxicity. Cardiologists and oncologists met recently to discuss strategies and future research directions for addressing these side effects.
-
Nivolumab and Ipilimumab Effective against Melanoma That Has Spread to the Brain
Results from a clinical trial show that the combination of nivolumab (Opdivo) and ipilimumab (Yervoy) halted the growth of or shrank metastatic brain tumors in more than half of participants with melanoma that had spread to the brain.
-
Moxetumomab Approved by FDA for Hairy Cell Leukemia
The FDA has approved moxetumomab pasudotox (Lumoxiti), a bacterial toxin–based drug, for the treatment of some patients with hairy cell leukemia (HCL). Moxetumomab is approved to treat patients with HCL who have already undergone at least two lines of standard treatments.
-
Integrating Geriatric Assessment into Cancer Care: A Conversation with Dr. Supriya Mohile
Dr. Supriya Mohile discusses the unique issues experienced by older adults with cancer and efforts to incorporate geriatric assessment into patient care, including the publication of recent ASCO clinical guidelines on geriatric cancer care.