Clinical Trial Results - Cancer Currents Blog
Reports on findings from cancer clinical trials, with commentary from leading researchers on how the trial results will affect patient care.
-
Durvalumab Extends Lives of People with Early-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
The immunotherapy drug durvalumab (Imfinzi) can help people with early-stage small cell lung cancer live longer, results from a large clinical trial show. Three years after starting treatment, nearly 60% of people who received the drug were still alive.
-
Pembrolizumab Is First Adjuvant Therapy to Improve Overall Survival in Kidney Cancer
In a large clinical trial, treatment with pembrolizumab after surgery helped people with kidney cancer live longer than those who got a placebo and standard monitoring. The findings mark the first time an adjuvant treatment for kidney cancer has improved survival.
-
New Approach May Help People with Cancer Better Manage Depression, Pain, and Fatigue
Assessing and offering people with cancer stepped collaborative care may help better manage symptoms of depression, pain, and fatigue than the standard referral to providers for treatment, according to a recent study.
-
Alectinib Approved as an Adjuvant Treatment for Lung Cancer
FDA has approved alectinib (Alecensa) as adjuvant therapy for people with lung cancer who have ALK-positive tumors. In a clinical trial, alectinib helped people live longer after surgery without their cancer returning than chemotherapy.
-
Approval of Elahere Expands Treatment Options for Some Advanced Ovarian Cancers
FDA approved mirvetuximab soravtansine-gynx (Elahere) to treat people with advanced, platinum-resistant ovarian cancer whose tumors overproduce a protein called FR-α. The full approval was based on the results of a large, randomized trial called MIRASOL, which showed Elahere improved survival for these people.
-
Simple Hysterectomy May Expand Treatment Options for Early-Stage Cervical Cancer
For some people with early-stage cervical cancer, a surgical procedure called a simple hysterectomy may be a safe and effective alternative to treatment with a radical hysterectomy, results from the SHAPE trial show.
-
Nivolumab Injections Could Make Treatment Easier for More People with Cancer
In a clinical trial, an injectable form of nivolumab (Opdivo) was as effective against kidney cancer as the intravenous form of the drug. Side effects were also similar and treatment time was shorter. Injectable immunotherapies, several experts said, if found to be comparable to IV forms, can be more convenient to receive and accessible to more people.
-
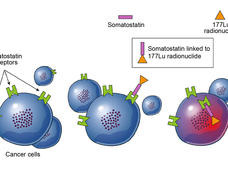
Lutathera Shows Promise as Part of Initial Therapy for Some Neuroendocrine Tumors
Adding Lu 177-dotate to the initial treatment of certain advanced neuroendocrine tumors nearly tripling the length of time people survive without their tumors getting worse, according to new clinical trial results.
-
Repotrectinib Expands Treatment Options for Lung Cancers with ROS1 Fusions
The results of the clinical trial that led to FDA’s 2023 approval of repotrectinib (Augtyro) for lung cancers with ROS1 fusions have been published. The drug shrank tumors in 80% of people receiving the drug as an initial treatment.
-
Can Some People with Breast Cancer Safely Skip Lymph Node Radiation?
Some people with no evidence of cancer in nearby lymph nodes after presurgical chemotherapy can skip radiation to that area without increasing the risk of the cancer returning, a clinical trial found. But some experts caution that more details are needed.
-
Trial Results Support Adding Daratumumab to Initial Treatment for Multiple Myeloma
Adding daratumumab (Darzalex) to standard treatment helped people with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma live longer without their cancer getting worse or dying. People taking daratumumab were also more likely to have no detectable signs of cancer (minimal residual disease) after treatment.
-
Enzalutamide Gets Added Approval for Prostate Cancer That Hasn’t Spread
Under a new FDA approval, enzalutamide (Xtandi) can now be used alone, or in combination with leuprolide, to treat people with nonmetastatic prostate cancer that is at high risk of returning after surgery or radiation.
-
Toripalimab Becomes First Immunotherapy Drug Approved for Nasopharyngeal Cancer
FDA approved toripalimab (Loqtorzi) based on the results of a large clinical trial showing that, when added to chemotherapy, the drug extended survival in people with nasopharyngeal cancer that returned after initial treatment or spread in the body.
-
Following Abnormal Cancer Screening Results, Multi-Level Reminders May Increase Follow-Up
In a clinical trial, a simple letter and phone call helped increase the number of people who completed the recommended follow-up testing after an abnormal cancer screening result.
-
Virtual Mind–Body Fitness Classes Show Unexpected Benefit in People with Cancer
In a clinical trial, people being treated for cancer who participated in virtual mind–body fitness classes were less likely to be hospitalized, and had shorter stays when they were hospitalized, than people who did not take the classes.
-
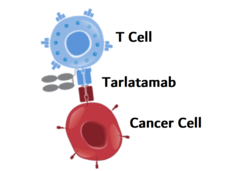
Tarlatamab Shows Promise for Some People with Small Cell Lung Cancer
Tarlatamab, a new type of targeted immunotherapy, shrank small cell lung cancer (SCLC) tumors in more than 30% of participants in an early-stage clinical trial. Participants had SCLC that had progressed after previous treatments with other drugs.
-
Groundbreaking Trial Results Expand Treatment Options for Some People with Bladder Cancer
For the first time in decades, people with advanced bladder cancer have more effective treatment options. New clinical trial results mark a pivotal moment following years of little progress, bladder cancer experts believe.
-
FDA Amends Approval of Pembrolizumab to Treat Stomach and Esophageal Junction Cancer
FDA has changed its 2021 approval of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) along with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and chemotherapy for treating HER2-positive stomach or GEJ cancer. The agency also announced a new approval of pembrolizumab for HER2-negative forms of these same cancers.
-
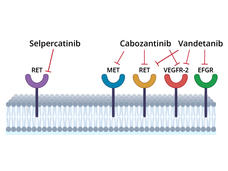
Selpercatinib Slows Progression of RET-Positive Lung, Medullary Thyroid Cancers
For people with lung cancer and medullary thyroid cancer whose tumors have changes in the RET gene, selpercatinib improved progression-free survival compared with other common treatments, according to new clinical trial results.
-
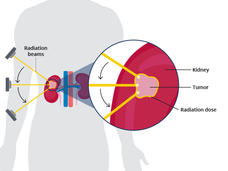
SBRT Emerging as an Important Treatment for Early-Stage Kidney Cancer
Stereotactic body radiotherapy was effective in people with localized kidney cancer who weren’t able to have surgery to remove their tumor, a clinical trial has shown. No patients had their cancer start growing or died from cancer over the next 5 years.