July 2022 - Cancer Currents Blog
-
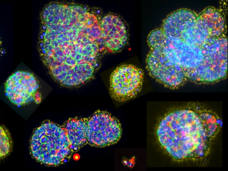
New Cancer Model Shows Promise in Predicting If Treatment Will Shrink Tumors
A research team hopes to offer oncologists a new tool to guide treatment choices for their patients. In a small study, a tumor model called micro-organospheres accurately predicted whether patients would respond to their chemotherapy treatment.
-
Disguising Cancer as an Infection Helps the Immune System Eliminate Tumors
NCI researchers are developing an immunotherapy that involves injecting protein bits from cytomegalovirus (CMV) into tumors. The proteins coat the tumor, causing immune cells to attack. In mice, the treatment shrank tumors and kept them from returning.
-
Dabrafenib–Trametinib Combination Approved for Solid Tumors with BRAF Mutations
FDA has approved the combination of the targeted drugs dabrafenib (Tafinlar) and trametinib (Mekinist) for nearly any type of advanced solid tumor with a specific mutation in the BRAF gene. Data from the NCI-MATCH trial informed the approval.
-
Androgen Receptor May Explain Sex Differences in Melanoma Treatment Response
Male patients with metastatic melanoma don’t live as long as females, and their tumors are more likely to become resistant to commonly used treatments. A new study may help explain why: the androgen receptor.
-
Immunotherapy’s Skin Side Effects: Are Microbes to Blame?
People with cancer who take immunotherapy drugs often develop skin side effects, including itching and painful rashes. New research in mice suggests these side effects may be caused by the immune system attacking new bacterial colonies on the skin.
-
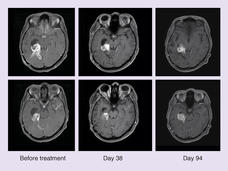
Ifosfamide May Be Treatment of Choice for Some People with Ewing Sarcoma, Trial Shows
New findings from the first large, randomized clinical trial to compare chemotherapy regimens for relapsed or treatment-resistant Ewing sarcoma could help doctors and patients select treatments.
-
Enhertu Improves Survival for Metastatic “HER2-Low” Breast Cancer
People with metastatic breast cancer whose tumors had low levels of HER2 protein lived longer after treatment with trastuzumab deruxtecan (Enhertu) than those treated with standard chemotherapy, results of the DESTINY-Breast04 clinical trial show.