Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute.
-
Brentuximab May Mean Less Radiation for Children, Teens with Hodgkin Lymphoma
In a recent study, a treatment regimen using brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) instead of the chemotherapy drug vincristine allowed some children and teens with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma to avoid radiation therapy—and the long-term health problems that can come with it.
-
Topotecan–Berzosertib Combination Shows Promise against Small Cell Lung Cancer
Combining the chemotherapy drug topotecan and the investigational drug berzosertib shrank tumors in some patients with small cell lung cancer, results from an NCI-supported phase 1 clinical trial show. Two phase 2 trials of the combination are planned.
-
Study Details Long-Term Side Effects of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
While doctors are familiar with the short-term side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors, less is known about potential long-term side effects. A new study details the chronic side effects of these drugs in people who received them as part of treatment for melanoma.
-
Immunotherapy Drug Tebentafusp Improves Survival in Advanced Uveal Melanoma
In a large trial, tebentafusp helped patients with uveal melanoma live longer than patients who received other treatments for the disease. Uveal melanoma is an aggressive cancer of the eye, and many patients do not survive for a year once it has spread.
-
Can Acupuncture Help Cancer Survivors with Chronic Pain?
In a large clinical trial, cancer survivors treated with acupuncture had modest improvements in chronic pain compared with those who received standard pain treatments. The study couldn’t rule out a placebo effect for the improvement with acupuncture.
-
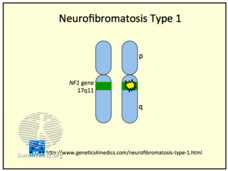
NF1 Associated with More Cancer Types Than Previously Known
The study also found that people with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) developed some cancers at an earlier age and were more likely to die from several cancer types, which make preventive measures and early diagnosis important for people with NF1.
-
FDA Approves BCMA-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy for Multiple Myeloma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved idecabtagene vicleucel (Abecma) for some people with multiple myeloma. The approval is based, in part, on a small study in which ide-cel partially or completely shrank tumors in 72% of patients.
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing Could Help Guide AML Treatment
For people with acute myeloid leukemia and related cancers, a new study shows whole-genome sequencing could replace a series of conventional tests used to help guide decisions about treatment.
-
Researchers Create Modified Antibodies to Target RAS and p53 in Cancer
Researchers have developed synthetic antibodies, called diabodies, that block the activity of two of the most notorious cancer-related proteins, RAS and p53. In experiments in mice, the synthetic antibodies shrank tumors with these mutated proteins.
-
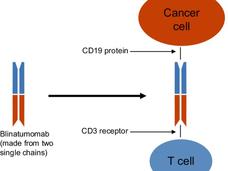
Blinatumomab Improves Survival in Children with Relapsed Leukemia
The results of two trials establish blinatumomab (Blincyto) as a new standard treatment for children and young adults with high-risk relapsed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia after remission has been achieved and before a stem cell transplant.
-
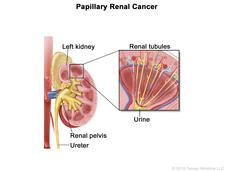
Targeted Therapy Cabozantinib Slows Progression of Rare Kidney Cancer
Cabozantinib (Cabometyx) is an effective initial treatment for people with metastatic papillary renal cell carcinoma (PRCC), a rare type of kidney cancer. A clinical trial showed the drug was more effective than the current standard treatment.
-
Texting May Help Reduce Disparities in Colorectal Cancer Screening
Combining text messaging with mailing people free at-home FIT kits helped increase screening for colorectal cancer among a predominantly Black population, a new study has found. It’s part of a larger effort to reduce disparities in cancer screening.
-
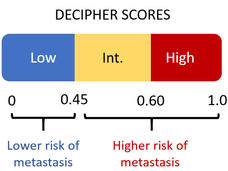
Hormone Therapy for Prostate Cancer? A Genetic Test Could Help Decide
For some men with prostate cancer, a genetic biomarker test called Decipher may help predict if their cancer will spread elsewhere in the body. The test could help determine whether hormone therapy, which can cause distressing side effects, is needed.
-
Commemorating the Contributions of Cancer Research Greats
Following the death of Dr. Emil Freireich in February, NCI Director Norman E. Sharpless reflects on the accomplishments and legacies of Dr. Freireich and several other cancer research luminaries who have passed in recent years.
-
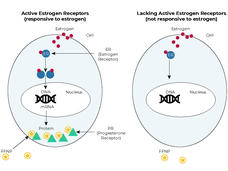
Imaging Test Could Help Guide Breast Cancer Treatment Decisions
For some people with ER-positive breast cancer, a new imaging test may help guide decisions about receiving hormone therapy, according to a new study. The test can show whether estrogen receptors in tumors are active and responsive to estrogen.
-
For Cancer Screening, COVID-19 Pandemic Creates Obstacles, Opportunities
After a steep drop in screening for common cancers early in the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers are now exploring ways to improve cancer screening during the current crisis and beyond.
-
Oncotype DX Breast Cancer Test May Be Less Accurate for Black Patients
The test, which helps guide treatment decisions, was not as good at predicting the risk of death from breast cancer for Black patients as for White patients, a new study has found. The findings highlight the need for greater racial diversity in research studies.
-
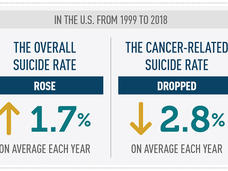
Rate of Suicides Related to Cancer Is Declining
Cancer-related suicides dipped each year between 1999 and 2018 in the United States, a recent study has found. Yet, people who have had cancer remain at high risk for suicide and improvements in supportive care are needed, experts say.
-
Cancer Researchers Bring Tools, Experience to COVID-19 Studies
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began, cancer researchers have brought their expertise to coronavirus studies. Their findings have ranged from insights into how the SARS-CoV-2 virus enters cells to the identification of potential COVID-19 therapies.
-
Commemorating and Making History: The National Cancer Act 50th Anniversary
The week after the globe recognized World Cancer Day and NCI staff were honored with a virtual visit from First Lady Dr. Jill Biden, the NCI director kicks off the commemoration of the 50th anniversary of the National Cancer Act of 1971.