What are dense breasts?
Breasts contain glandular tissue, fibrous connective tissue, and fatty breast tissue. Breast density is a term that describes the relative amount of these different types of breast tissue as seen on a mammogram. Dense breast tissue has relatively high amounts of glandular tissue and fibrous connective tissue and relatively low amounts of fatty breast tissue.
Are dense breasts common?
Yes, dense breasts are common. Nearly half of all women who are 40 and older who get mammograms are found to have dense breast tissue.
What factors influence breast density?
Breast density is often inherited, but other factors can influence it.
- Factors associated with higher breast density include using menopausal hormone therapy and having a low body mass index.
- Factors associated with lower breast density include increasing age and having children.
How do I know if I have dense breasts?
Dense breast tissue cannot be felt by a woman, such as during a breast self-exam, or by her doctor during a clinical breast exam. Only a radiologist looking at a mammogram can tell if a woman has dense breasts. Dense breasts are sometimes called mammographically dense breasts.
How is breast density categorized in a mammogram report?
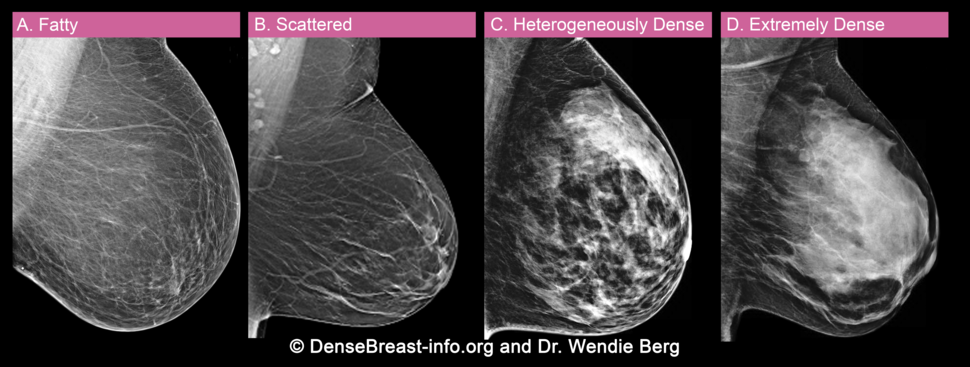
Doctors use the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) to classify breast density. This system, developed by the American College of Radiology, helps doctors interpret and report back mammogram findings. Doctors who review mammograms are called radiologists. BI-RADS classifies breast density into four categories:
- Entirely fatty breast tissue: There is almost all fatty breast tissue. It is found in about 10% of women.
- Scattered fibroglandular breast tissue: There is mostly fatty tissue with some areas of dense glandular and fibrous connective tissue. It is found in about 40% of women.
- Heterogeneously dense breast tissue: There are many areas of dense glandular and fibrous connective tissue, with some areas of fatty tissue. It is found in about 40% of women.
- Extremely dense breast tissue: There is almost all dense glandular and fibrous connective tissue. It is found in about 10% of women.
If your mammogram report letter says you have dense breasts, it means that you have either heterogeneously dense breast tissue or extremely dense breast tissue.
Does having dense breast tissue affect a mammogram?
Dense breasts can make a mammogram more difficult to interpret. That's because dense breast tissue and some abnormal breast changes, such as calcifications and tumors, both appear as white areas in the mammogram, whereas fatty tissue appears as dark areas.
As a result, mammography is less sensitive in women with dense breasts—that is, it is more likely to miss cancer. Women with dense breasts may be called back for follow-up testing more often than women with fatty breasts.
Are dense breasts a risk factor for breast cancer?
Dense breasts are not considered an abnormal breast condition or a disease. However, dense breasts are a risk factor for breast cancer. That is, women with dense breasts have a higher risk of breast cancer than women with fatty breasts. This risk is separate from the effect of dense breasts on the ability to read a mammogram. Learn more about other risk factors for breast cancer as well as protective factors for breast cancer.
Updated FDA regulations require mammography providers to inform women if they have dense breasts.
Should women with dense breasts have additional screening for breast cancer?
There is not yet enough evidence to recommend for or against additional imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI to screen for breast cancer in women with dense breasts, according to the Recommendation Statement on Breast Cancer Screening by the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF). Talk with your doctor or nurse to learn more about your options.
Are breast cancer patients with dense breasts more likely to die from breast cancer?
No. Research has found that breast cancer patients who have dense breasts are no more likely to die from breast cancer than breast cancer patients who have fatty breasts, after accounting for other health factors and tumor characteristics.
Questions to consider asking your doctor or nurse
Ask these questions to get information that’s specific to you, based on your personal medical history:
- Do I have dense breasts, based on my most recent mammogram result?
- Do you recommend additional screening for me? What are the benefits and drawbacks of these additional tests?
- What is my personal risk of breast cancer, given my risk factors and protective factors?
Are there clinical trials for women with dense breasts?
Yes, there are ongoing and completed clinical trials related to dense breasts that are studying better ways to detect breast cancer in women with dense breasts. You can also contact NCI’s Cancer Information Service to get tailored clinical trial searches related to breast density and breast cancer screening.
Questions that researchers are asking about the relationship between breast density and breast cancer
- What biomarkers or molecular markers can be identified to better characterize dense breast tissue and predict a woman's risk for breast cancer?
- Are certain patterns or areas of dense breast tissue particularly risky?
- How does the microenvironment of dense breast tissue affect the development and growth of tumors?
- Are changes in breast density over time associated with changes in breast cancer risk?
- Could women with dense breasts lower their breast density and risk of developing breast cancer by exercising, taking drugs such as low dose tamoxifen, or applying topical agents?
- Could imaging tests such as ultrasound, contrast enhanced mammography, MRI (such as diffusion-weighted MRI or fast MRI), or molecular breast imaging help find breast cancer in women with dense breasts?
NCI’s Division of Cancer Epidemiology and Genetics conducts research on breast density and breast cancer risk factors.
NCI's Division of Cancer Prevention supports research on cancer screening and risk factors, including breast density, to help researchers learn about the best way to find breast cancer in women who have no symptoms.
NCI’s Division of Cancer Control and Population Sciences supports research such as the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) Breast Working Group. CISNET is a consortium of NCI-sponsored investigators conducting simulation modeling to improve our understanding of the impact of prevention, screening, and treatment on population trends in incidence and mortality.