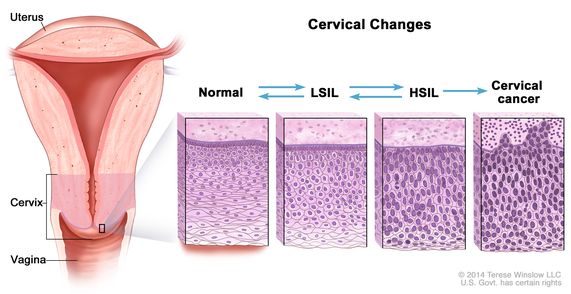
low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion
(... SKWAY-mus IN-truh-eh-pih-THEE-lee-ul LEE-zhun)
An area of abnormal cells that forms on the surface of certain organs, such as the cervix, vagina, vulva, anus, and esophagus. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions look slightly abnormal when looked at under a microscope. They are usually caused by infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and are found when a Pap test or biopsy is done. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions usually go away on their own without treatment, but sometimes they can become cancer and spread into nearby tissue. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion is sometimes called mild dysplasia. Also called LSIL.