Cancer Genetics Overview (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version
Introduction
Cancer risk is influenced by multiple factors, including genetics, environment, medical history, and lifestyle. The content in PDQ Cancer Genetics summaries covers evidence on inherited genetic risk factors, including the cancer risks and management associated with hereditary cancer syndromes (including pathogenic variants in specific genes that cause them). Knowledge of genetic components that contribute to cancer risk rapidly improves our understanding of cancer biology and helps identify individuals with increased cancer risk. These findings enhance the ability to characterize malignancies, establish treatment tailored to the molecular fingerprint of specific cancers, and lead to the development of new therapeutic modalities. As a consequence, this expanding knowledge base has implications for all aspects of cancer management, including prevention, screening, and treatment.
Family histories of cancer can help identify individuals who are at increased risk of developing cancer and select candidates for hereditary cancer genetic testing. Genetic testing results can indicate that individuals have increased cancer risk or that a cancer has an underlying genetic predisposition.
Cancer Genetics Concepts and Terminology
The term, variant, describes a difference (i.e., genetic change) between an individual or a group of individuals who are being studied and the DNA reference sequence. The term, mutation, is sometimes still used in patient settings. Variants are classified as benign (harmless), likely benign, of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, or pathogenic (affects gene function and is disease-associated). For more information, see Table 1.
The cancers associated with pathogenic variants and the risk estimates to develop cancer continue to be updated based on current research. Risk updates even occur for genes that have been studied for many years, like the Lynch syndrome genes.
This section discusses concepts and terminology used in hereditary cancer genetics. For additional terms, see the National Cancer Institute's Dictionary of Genetics Terms.
Levels of Cancer Risk
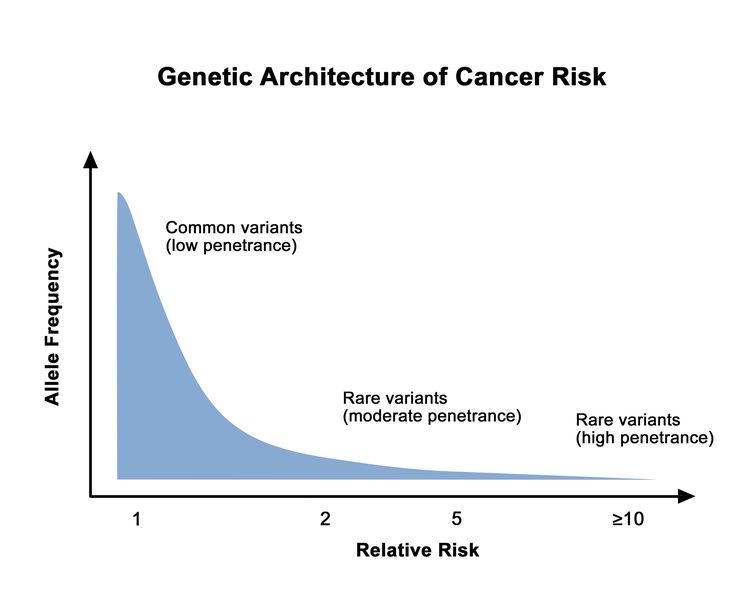
Different hereditary cancer genes are associated with varying levels of cancer risk. This cancer risk can also vary among pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants in the same gene. Rare genetic variants are generally associated with higher cancer risks than common genetic variants. This is depicted in Figure 1.
In some genes, P/LP variants increase an individual's risk of developing cancer at a younger age than that typically seen in the general population.
Cancer risk is multifactorial. It is influenced by genetic, environmental, medical, and lifestyle factors. These nongenetic factors impact cancer risk in individuals who carry a P/LP variant in genes like BRCA1 or BRCA2. For more information, see the Introduction and the Polygenic risk scores for breast and ovarian cancer sections in Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers.
Available genetic testing expands as more genetic variants are identified and their associated cancer risks are characterized.
Associated Cancers
Cancer risks vary based on the hereditary cancer gene and pathogenic variant involved. For example, P/LP variants in BRCA1 and BRCA2 are associated with breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and other cancers.
Types of Genetic Variants in the Context of Cancer Genetics
- Germline variant: A variant in a reproductive cell (i.e., egg or sperm) that is in the DNA of every cell in the offspring's body. A variant contained within the germline can be passed from parent to offspring and is, therefore, hereditary.
- Somatic (acquired) variant: In the context of cancer genetics, somatic variant refers to a variant in DNA that occurs before or during tumor development. This type of variant is not present within the germline (i.e., sperm and egg).
[Note: Somatic variants have various nuances, like the concepts of mosaicism, gonadal mosaicism, and clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential.]
For more information about germline genetic testing and somatic genetic testing, see the Clinical Applications section.
Variant Classifications for Hereditary Cancer Genetic Testing
Variants (i.e., genetic changes) are classified as pathogenic, likely pathogenic, of uncertain significance, benign, or likely benign.[1] Variant classification is based on whether a variant is associated with disease. Genetic variant studies research how variants are associated with specific diseases.
| Type of Variant | Description |
|---|---|
| Adapted from Richards et al.[1] | |
| Pathogenic | The variant is expected to affect gene function and is disease-associated. Additional evidence is not expected to alter the classification of this variant (probability of being pathogenic > 0.99). [Note: Not all pathogenic variants are fully penetrant.][2] |
| Likely pathogenic | The variant is likely expected to affect gene function and is likely disease-associated (probability of being pathogenic, 0.95–0.99).[2] |
| Uncertain significance | There is not enough information when the variant is evaluated to support a more definitive classification (probability of being pathogenic, 0.05–0.949).[2] |
| Likely benign | The variant is likely not expected to affect gene function and is likely not disease-associated (probability of being pathogenic, 0.001–0.049).[2] |
| Benign | The variant is not expected to affect gene function and is not disease-associated (probability of being pathogenic < 0.001).[2] |
Variants may be referred to as secondary or incidental findings:
- Secondary findings: Variants found during genetic testing that were intentionally analyzed but are not related to the indication for which the exome or genome sequencing was ordered. These findings may have clinical utility for the ordering physician, the patient, or the patient's family. (Adapted from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomic [ACMG]'s recommendations for reporting incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing.) ACMG has adopted secondary findings, rather than incidental findings, as its standard terminology when reporting exome or genome results.
- Incidental findings: Variants that were discovered during genetic testing unintentionally or accidentally.[3]
Inheritance Patterns for Hereditary Cancer Risk
Hereditary cancer risk is inherited differently, depending on the indicated gene. Most hereditary cancer risks are inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. In autosomal dominant inheritance, an individual is at risk to develop cancer when he/she inherits one pathogenic variant (in one of the two copies of the gene). Some hereditary cancer syndromes have other inheritance patterns (e.g., MUTYH-associated polyposis is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion).
For more information about how to recognize hereditary cancer inheritance patterns, see the Analysis of the family history section in Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling.
References
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al.: Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17 (5): 405-24, 2015. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Plon SE, Eccles DM, Easton D, et al.: Sequence variant classification and reporting: recommendations for improving the interpretation of cancer susceptibility genetic test results. Hum Mutat 29 (11): 1282-91, 2008. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Kalia SS, Adelman K, Bale SJ, et al.: Recommendations for reporting of secondary findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing, 2016 update (ACMG SF v2.0): a policy statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 19 (2): 249-255, 2017. [PUBMED Abstract]
Identifying Individuals for Hereditary Cancer Genetic Testing
Correctly identifying individuals/families with increased risk of developing cancer is an important role of primary care physicians and other health care providers. Once identified, these individuals can be referred to genetic counseling, where the following can be discussed: risk assessment, possible genetic testing, and developing a management plan. Clues suggesting hereditary cancer risk include the following: an individual/family member is diagnosed with cancer at a young age, cancers in the family exhibit a Mendelian inheritance pattern (most often autosomal dominant inheritance), and multiple primary cancers occur in the same patient/family member. Hereditary cancer can also be a component of a broader syndromic phenotype. For more information about cancer risk assessment and features suggestive of hereditary cancer, see Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling.
Implications of Identifying a Hereditary Predisposition to Cancer
Identifying individuals with increased hereditary cancer risk may inform future cancer screening, surveillance, risk-reducing options, and if applicable, treatment.[1,2] Some examples of these management options include the following:
- Increased frequency of screening and/or screening at an earlier age than that in general population recommendations (e.g., beginning colonoscopy screening before age 45 y).
- Interventions to reduce the risk of developing cancer (e.g., tamoxifen to reduce breast cancer risk, risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy to reduce ovarian cancer risk).
- Treatment implications for individuals diagnosed with cancer (i.e., poly [ADP-ribose] polymerases [PARP] inhibitors for breast cancer in individuals with BRCA1/BRCA2 pathogenic/likely pathogenic [P/LP] variants).
A hereditary cancer risk assessment can also inform an individual's future plans (e.g., lifestyle changes, family planning).
Identifying hereditary cancer risk also provides information to an individual’s family members. When an individual has a hereditary cancer P/LP variant, his/her relatives can have targeted genetic testing to search for this specific familial variant. This is known as cascade genetic testing and can help clarify cancer risk in the proband's family members. For more information about cascade genetic testing, see the Cascade Genetic Testing of Family Members section in Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling.
Family members who pursue genetic testing can learn either of the following:
- They carry the P/LP variant identified in their family. These patients can discuss appropriate cancer risk-management measures with their medical team.
- They do not carry the P/LP variant identified in their family. Cancer screening for these patients will be based on other cancer risk factors (e.g., environmental exposures, cancer in the family that is not related to the P/LP variant).
References
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal. Version 2.2023 . Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2023. Available with free registration. Last accessed March 13, 2024.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, and Pancreatic. Version 3.2024. Plymouth Meeting, Pa: National Comprehensive Cancer Network, 2023. Available online with free registration. Last accessed November 13, 2024.
Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Genetic Counseling
A cancer genetics risk assessment includes an evaluation of an individual’s personal history and family history.[1,2] For detailed information about cancer genetics risk assessment, see Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling.
Informed consent is an important part of the genetic testing process. For more information about informed consent, see the Informed Consent section in Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling.
Cancer genetics risk assessment and counseling often involves a multidisciplinary team of health professionals. These individuals may include a genetics professional (i.e., genetic counselor, advanced-practice genetics nurse, or medical geneticist), and additional medical experts may also be included (i.e., oncologist, surgeon, and/or internist).
Genetic counseling is a meeting between health care professionals and patients in which patients learn about genetic health and available genetic testing and management options. These health professionals also provide individuals with support, as they attempt to understand and incorporate this genetic information into their daily lives. Genetic counseling generally involves six steps:
- Medical history and family history assessment.
- Analysis of genetic information.
- Communication of genetic information.
- Education about inheritance, genetic testing, management, risk-reduction options, resources, and research opportunities.
- Supportive counseling to facilitate informed decision making and adaptation to the risk or condition.
- Follow-up.
Genetic counselors are health care professionals with highly-specialized training in genetic education and genetic counseling. Genetic counselors help patients make personalized, informed decisions about hereditary risk. Genetic counseling can also be provided by physicians, nurses, or other health care providers who have advanced training in genetics.
A list of practicing Genetic counselors can be found on the National Society of Genetic Counselors' website and the American Board of Genetic Counseling's website.
In some hereditary cancer syndromes, patients develop clinical manifestations that are not related to cancer. In these cases, a medical genetics evaluation may be indicated and conducted by a physician who has completed residency training in the following: 1) a primary care specialty (pediatrics, internal medicine, obstetrics/gynecology, family medicine, etc.), and 2) clinical genetics. A geographic listing of certified clinical geneticists can be obtained on the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics' website.
A medical genetics evaluation includes a comprehensive review of the patient’s medical history (from conception to present day), review of medical records, a dysmorphology examination, assessment of the patient's family history, and review of available diagnostic testing (including genetic testing, if warranted). The dysmorphology examination identifies physical features that are characteristic of certain hereditary cancer syndromes but are not necessarily cancerous lesions. For example, this examination may identify unusual skin pigmentation (or other distinct dermatologic findings), small/large head circumference, or other physical differences. A medical geneticist may also play a role in the patient's medical management.
References
- Berliner JL, Cummings SA, Boldt Burnett B, et al.: Risk assessment and genetic counseling for hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes-Practice resource of the National Society of Genetic Counselors. J Genet Couns 30 (2): 342-360, 2021. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Holter S, Hall MJ, Hampel H, et al.: Risk assessment and genetic counseling for Lynch syndrome - Practice resource of the National Society of Genetic Counselors and the Collaborative Group of the Americas on Inherited Gastrointestinal Cancer. J Genet Couns 31 (3): 568-583, 2022. [PUBMED Abstract]
Genes and Syndromes Associated With Hereditary Cancer Risk
Cancer type–specific information and hereditary cancer genes/syndromes are discussed in the following PDQ Cancer Genetics summaries:
- Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers: Includes information on BRCA1/BRCA2, Lynch syndrome (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM genes), PALB2, Li-Fraumeni syndrome (TP53 gene), hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (CDH1 gene), moderate-risk genes, and other hereditary breast and gynecologic cancer genes/syndromes.
- Genetics of Colorectal Cancer: Includes information on Lynch syndrome (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM genes), familial adenomatous polyposis (APC gene), MUTYH-associated polyposis (MUTYH gene), and other hereditary colorectal cancer genes/syndromes.
- Genetics of Endocrine and Neuroendocrine Neoplasias: Includes information on multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) (MEN1 gene), MEN2, MEN4 (CDKN1B gene), familial pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma syndrome (SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD genes and others), Carney-Stratakis syndrome (SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD genes), and familial nonmedullary thyroid cancer.
- Genetics of Gastric Cancer: Includes information on hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (CDH1 and CTNNA1 genes) and other hereditary gastric cancer syndromes.
- Genetics of Hereditary Hematologic Malignancies: Includes several genes and hereditary syndromes associated with hematologic malignancies.
- Genetics of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Includes information on Von Hippel-Lindau disease (VHL gene), hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (FH gene), hereditary papillary renal carcinoma (MET gene), and Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (FLCN gene).
- Genetics of Prostate Cancer: Includes information on BRCA1/BRCA2, HOXB13, Lynch syndrome (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, EPCAM genes), ATM, and CHEK2.
- Genetics of Skin Cancer: Includes information on several genes and hereditary syndromes associated with basal cell carcinoma (such as basal cell nevus syndrome [PTCH1, SUFU, PTCH2 genes]), squamous cell carcinoma (such as epidermolysis bullosa), and melanoma (such as CDKN2A, MITF, and BAP1 genes).
The following gene/syndrome-specific summaries are also available:
- BRCA1 and BRCA2: Cancer Risks and Management.
- Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer.
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Proximal Polyposis of the Stomach (GAPPS).
- Von Hippel-Lindau Disease.
- Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer.
- Hereditary Papillary Renal Carcinoma.
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome.
- RUNX1-Familial Platelet Disorder.
- CEBPA-Associated Familial Acute Myeloid Leukemia.
- DDX41-Associated Myeloid Malignancies.
- GATA2 Deficiency Syndrome.
- Rhabdoid Tumor Predisposition Syndrome Type 1.
Methods of Genetic Analysis and Gene Discovery
The methods in this section provide a brief background about the genetic analysis and discovery approaches that have been used during the past 10 to 30 years to identify disease susceptibility genes. These methods led to the discovery of important cancer genes like BRCA1, BRCA2, and other breast cancer risk genes. Since then, genetic analysis techniques have transitioned to next-generation sequencing methods, as described in the Clinical Sequencing section of this summary.
Linkage Analyses
Since it was recognized that cancer clusters in families, investigators have collected data on families with multiple cancer cases. The investigators aimed to localize cancer susceptibility genes via linkage studies.
Linkage studies are typically performed on high-risk kindreds, in whom multiple cases of a particular disease have occurred, in an effort to identify disease susceptibility genes. Linkage analysis statistically compares the genotypes between affected and unaffected individuals. Linkage analysis also seeks evidence that known genetic markers are inherited along with the disease trait. If such evidence is found (linkage), it provides statistical data that the chromosomal region near the known genetic marker also harbors a disease susceptibility gene. Once a genomic region of interest has been identified through linkage analysis, additional studies are required to prove that there truly is a susceptibility gene at this position. Linkage analysis is affected by the following:
- Family size and having enough family members to contribute DNA.
- The number of disease cases in each family.
- Factors related to age at disease onset (e.g., screening use).
- Gender differences in disease risk (not relevant in gender-specific cancers).
- Heterogeneity of disease in cases (e.g., aggressive vs. nonaggressive phenotype).
- The accuracy of family history information.
- Prevalence of phenocopies.
An additional issue in linkage studies is the background rate of sporadic cancer in the context of family studies. For example, because a man’s lifetime risk of prostate cancer is one in eight,[1] it is possible that families under study have both inherited and sporadic prostate cancer cases. Thus, a male may still develop prostate cancer, even if he does not inherit the prostate cancer susceptibility gene that is present in his family. Hence, studies have addressed inconsistencies between linkage data by requiring strict inclusion criteria that define clinically significant disease.[2-6] This approach attempts to define a homogeneous set of cases/families to increase the likelihood of identifying a linkage signal.
Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS)
GWAS are identifying common, low-penetrance susceptibility alleles for many complex diseases,[7] including cancer. This approach can be contrasted with linkage analysis, which searches for genetic-risk variants cosegregating within families that have a high prevalence of disease. While linkage analyses are designed to uncover rare, highly penetrant variants that segregate in predictable heritance patterns (e.g., autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked, and mitochondrial), GWAS are best suited to identify multiple, common, low-penetrance genetic polymorphisms. GWAS are conducted under the assumption that the genetic underpinnings of complex phenotypes, such as prostate cancer, are governed by many alleles, each conferring modest risk. Most genetic polymorphisms genotyped in GWAS are common, with minor allele frequencies greater than 1% to 5% within a given population (e.g., men of European ancestry). GWAS capture a large portion of common variation across the genome.[8,9] The strong correlation between many alleles located close to one another on a given chromosome (called linkage disequilibrium) allows one to “scan” the genome without having to test all 10 million known single nucleotide variants (SNVs). With GWAS, researchers can test approximately 1 million to 5 million SNVs per study and ascertain almost all common inherited variants in the genome.
In a GWAS, allele frequency for each SNV is compared between cases and controls. Promising signals—in which allele frequencies deviate significantly in case compared to control populations—are validated in replication cohorts. To have adequate statistical power to identify variants associated with a phenotype, large numbers of cases and controls, typically thousands of each, are studied. Because up to 1 million SNVs are evaluated in a GWAS, false-positive findings are expected to occur frequently when using standard statistical thresholds. Therefore, stringent statistical rules are used to declare a positive finding, usually using a threshold of P < 1 × 10-7.[10-12]
To date, thousands of cancer-risk variants have been identified by well-powered GWAS and validated in independent cohorts.[13] These studies have revealed consistent associations between specific inherited variants and cancer risk. However, the findings should be qualified with a few important considerations:
- GWAS reported thus far have been designed to identify relatively common genetic polymorphisms. It is very unlikely that an allele with high frequency in the population by itself contributes substantially to cancer risk. This, coupled with the polygenic nature of tumorigenesis, means that the contribution by any single variant identified by GWAS to date is quite small, generally with an odds ratio for disease risk of less than 1.3. In addition, despite extensive genome-wide interrogation of common polymorphisms in tens of thousands of cases and controls, GWAS findings to date do not account for even half of the genetic component of cancer risk.[14]
- Variants uncovered by GWAS are not likely to directly contribute to disease risk. As mentioned above, SNVs exist in linkage disequilibrium blocks and are merely proxies for a set of variants—both known and previously undiscovered—within a given block. The causal allele is located somewhere within that linkage disequilibrium block.
- Admixture by groups of different ancestry can confound GWAS findings (i.e., a statistically significant finding could reflect a disproportionate number of subjects in the cases versus controls, rather than a true association with disease). Therefore, GWAS are typically powered to analyze a single predominant ancestral group. As a result, some populations remain underrepresented in genome-wide analyses.
- The clinical relevance of variants identified from GWAS remains unclear. [15-17]
Implications of these points and how they relate to polygenic risk scores are discussed further in the Polygenic risk scores for breast and ovarian cancer section in Genetics of Breast and Gynecologic Cancers, the Genetic Polymorphisms and CRC Risk section in Genetics of Colorectal Cancer, and the Common Risk Variants and Polygenic Risk Scores for Prostate Cancer section in Genetics of Prostate Cancer.
References
- American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2025. American Cancer Society, 2025. Available online. Last accessed January 16, 2025.
- Stanford JL, McDonnell SK, Friedrichsen DM, et al.: Prostate cancer and genetic susceptibility: a genome scan incorporating disease aggressiveness. Prostate 66 (3): 317-25, 2006. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Chang BL, Isaacs SD, Wiley KE, et al.: Genome-wide screen for prostate cancer susceptibility genes in men with clinically significant disease. Prostate 64 (4): 356-61, 2005. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Lange EM, Ho LA, Beebe-Dimmer JL, et al.: Genome-wide linkage scan for prostate cancer susceptibility genes in men with aggressive disease: significant evidence for linkage at chromosome 15q12. Hum Genet 119 (4): 400-7, 2006. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Cancer risks in BRCA2 mutation carriers. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. J Natl Cancer Inst 91 (15): 1310-6, 1999. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Easton DF, Bishop DT, Ford D, et al.: Genetic linkage analysis in familial breast and ovarian cancer: results from 214 families. The Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium. Am J Hum Genet 52 (4): 678-701, 1993. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium: Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447 (7145): 661-78, 2007. [PUBMED Abstract]
- The International HapMap Consortium: The International HapMap Project. Nature 426 (6968): 789-96, 2003. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Thorisson GA, Smith AV, Krishnan L, et al.: The International HapMap Project Web site. Genome Res 15 (11): 1592-3, 2005. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Evans DM, Cardon LR: Genome-wide association: a promising start to a long race. Trends Genet 22 (7): 350-4, 2006. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Cardon LR: Genetics. Delivering new disease genes. Science 314 (5804): 1403-5, 2006. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Chanock SJ, Manolio T, Boehnke M, et al.: Replicating genotype-phenotype associations. Nature 447 (7145): 655-60, 2007. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Chang CQ, Yesupriya A, Rowell JL, et al.: A systematic review of cancer GWAS and candidate gene meta-analyses reveals limited overlap but similar effect sizes. Eur J Hum Genet 22 (3): 402-8, 2014. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Ioannidis JP, Castaldi P, Evangelou E: A compendium of genome-wide associations for cancer: critical synopsis and reappraisal. J Natl Cancer Inst 102 (12): 846-58, 2010. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Park JH, Gail MH, Greene MH, et al.: Potential usefulness of single nucleotide polymorphisms to identify persons at high cancer risk: an evaluation of seven common cancers. J Clin Oncol 30 (17): 2157-62, 2012. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Lindström S, Schumacher FR, Cox D, et al.: Common genetic variants in prostate cancer risk prediction--results from the NCI Breast and Prostate Cancer Cohort Consortium (BPC3). Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 21 (3): 437-44, 2012. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Wacholder S, Hartge P, Prentice R, et al.: Performance of common genetic variants in breast-cancer risk models. N Engl J Med 362 (11): 986-93, 2010. [PUBMED Abstract]
Clinical Sequencing
Introduction
Broad-scale genome sequencing approaches, including multigene (panel) testing, whole-exome sequencing (WES), and whole-genome sequencing (WGS), are rapidly being developed and incorporated into a spectrum of clinical oncologic settings, including cancer therapeutics and cancer risk assessment. Several institutions and companies offer tumor sequencing, and some are developing precision medicine programs that sequence tumor genomes to identify driver genetic alterations that are targetable for therapeutic benefit to patients.[1-3] Many of these tumor-based approaches use germline DNA sequences as a reference to discriminate between DNA changes only within the tumor and those that are potentially inherited. In the genetic counseling and cancer risk assessment setting, the use of multigene testing to evaluate inherited cancer risk is becoming more common and may become routine in the near future, with institutions and companies offering multigene testing to detect alterations in a host of cancer risk–associated genes.
These advances in gene sequencing technologies also identify variants in genes related to the primary indication for ordering genetic sequence testing, along with findings not related to the disorder being tested. The latter genetic findings, termed incidental or secondary findings, are currently a source of clinical, ethical, legal, and counseling debate. The American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues have published literature that address some of these issues and provide guidance and recommendations for their use.[4-7] However, controversy continues about when and what results to provide to patients and their health care providers. This section was created to provide information about genomic sequencing technologies in the context of clinical sequencing and highlights additional areas of clinical uncertainty for which further research and approaches are needed.
Background
DNA sequencing technologies have undergone rapid evolution, particularly since 2005 when massively parallel sequencing, or next-generation sequencing (NGS), was introduced.[8]
Automated Sanger sequencing is considered the first generation of sequencing technology.[9] Sanger cancer gene sequencing uses polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of genetic regions of interest followed by sequencing of PCR products using fluorescently labeled terminators, capillary electrophoresis separation of products, and laser signal detection of nucleotide sequence.[10,11] While this is an accurate sequencing technology, the main limitations of Sanger sequencing include low throughput, a limited ability to sequence more than a few genes at a time, and the inability to detect structural rearrangements.[10]
NGS refers to high throughput DNA sequencing technologies that are capable of processing multiple DNA sequences in parallel.[11] Although platforms differ in template generation and sequence interrogation, the overall approach to NGS technologies involves shearing and immobilizing DNA template molecules onto a solid surface, which allows separation of molecules for simultaneous sequencing reactions (millions to billions) to be performed in a parallel fashion.[10,12] Thus, the major advantages of NGS technologies include the ability to sequence thousands of genes at one time, a lower cost, and the ability to detect multiple types of genomic alterations, such as insertions, deletions, copy number alterations, and rearrangements.[10] Limitations include the possibility that specific gene regions may be missed, turnaround time can be lengthy (although it is decreasing), and informatics support to handle massive amounts of genetic data has lagged behind the sequencing capability. A well-recognized bottleneck to utilizing NGS data is the lack of advanced computational infrastructure to preserve, process, and analyze the vast amount of genetic data. The magnitude of the variants obtained from NGS is exponential; bioinformatics approaches need to evaluate genetic variants for predicted functional consequence in disease biology. There is also a need for user-friendly bioinformatics pipelines to analyze and integrate genetic data to influence the scientific and medical community.[11,13]
Clinical Applications
NGS has multiple clinical applications. In oncology, the two dominant applications are: 1) the assessment of somatic alterations in tumors to inform prognosis and/or targeted therapeutics; and 2) the assessment of the germline to identify cancer risk alleles.
Somatic testing
There are multiple approaches to tumor testing for somatic alterations. With targeted multigene testing, a number of different genes can be assessed simultaneously. These targeted multigene tests can differ substantially in the genes that are included, and they can be tailored to individual tumor types. Targeted multigene testing limits the data to be analyzed and includes only known genes, which makes the interpretation more straightforward than in whole exome or whole genome techniques. In addition, greater depth of coverage is possible with targeted multigene testing than with WES or WGS. Depth of coverage refers to the number of times a nucleotide has been sequenced; a greater depth of coverage has fewer sequencing errors. Deep coverage also aids in differentiating sequencing errors from single nucleotide polymorphisms.
WES and WGS are far more extensive techniques and aim to uncover variants in known genes and in genes not suspected a priori. The discovery of a variant that is unexpected for a particular tumor type can lead to the use of a directed therapeutic, which could improve patient outcome. WES generates sequence data of the coding regions of the genome (representing approximately 1% of the human genome), rather than the entire genome (WGS). Consequently, WES is less expensive than WGS.
Noncoding variants can be identified using WGS but cannot be identified using WES. The use of WGS is limited by cost and the vast bioinformatics needed for interpretation. Although the costs of sequencing have dropped precipitously, the analysis remains formidable.[14]
Although the goal of WES and WGS is to improve patient care by detecting actionable genetic variants (variants that can be targeted therapeutically), a number of issues warrant consideration. This testing may detect pathogenic variants, variants of uncertain significance (VUS), or no detectable abnormalities. In addition, pathogenic variants can be found in genes that are thought to be clearly related to tumorigenesis but can also be detected in genes with unclear relevance (particularly with WES and WGS approaches). VUS have unclear implications as they may, or may not, disrupt the function of the protein. The definition of actionable can vary, but often this term is used when an aberration, if found, would lead to recommendations against certain treatments (such as variants in ras) for which a clinical trial is available, or for which there is a known targeted drug. Although there are case reports of success with this approach, it is unlikely to be straightforward. Studies are ongoing.
Some commercial and single-institution assays test only the tumor. Clearly pathogenic variants found in important genes in the tumor can be somatic but could also be from the germline. In situations in which somatic analysis is paired with a germline analysis, it can be determined whether an identified alteration is inherited. A study that estimated the prevalence of germline variants from patients undergoing tumor sequencing with matched, normal DNA sequencing reported that cancer susceptibility genes were identified in 198 of 1,566 individuals (12.6%). Only 81 of these 198 individuals (40.9%) had pathogenic variants in cancer susceptibility genes concordant with their tumor type. When expanding to include known noncancer-related Mendelian disease genes, 246 of 1,566 individuals (15.7%) had pathogenic or presumed pathogenic germline variants identified.[15]
Sequencing tumors may lead to the identification of hereditary (germline) pathogenic variants.[16] Founder pathogenic variants in well-characterized cancer susceptibility genes are highly suggestive of a germline pathogenic variant. Hypermutated tumor phenotype may suggest an underlying constitutional defect in DNA repair. Clinical characteristics that fit with a particular genetic predisposition, such as family history, young age at diagnosis, or specific tumor type, may also raise the suspicion of a germline variant correlating with a tumor variant. A high variant allele fraction may also indicate a germline variant. All of these factors signify a potential need for patients to undergo genetic counseling and to consider confirmatory germline genetic testing.
The absence of a variant in a gene assessed as part of somatic testing does not rule out the presence of an inherited susceptibility. All patients whose personal and family histories are suggestive of hereditary cancer should consider germline testing regardless of their somatic results.
Ongoing clinical trials, such as the NCI Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH) Trial, are examining the value of somatic sequencing to find actionable targets. Germline sequencing is occurring as a component of this study.
Germline testing
The goal of germline testing is to identify pathogenic variants associated with an inherited risk of cancer and to guide cancer risk–management decisions. Also, germline testing can aid in some management decisions at the time of diagnosis (e.g., decisions about colectomy in Lynch syndrome–related colon cancer and contralateral mastectomy in carriers of BRCA1/BRCA2 pathogenic variants). In addition, there are emerging data that germline status may help determine systemic therapy (e.g., the use of cisplatin or poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase [PARP] inhibitors in BRCA1/BRCA2-related cancer).
Most germline genetic testing has been performed in a targeted manner, looking for variants in the gene(s) associated with a clinical picture (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2 in hereditary breast and ovarian cancer or the mismatch repair [MMR] genes in Lynch syndrome). However, targeted multigene tests available commercially or within an institution contain different sets of genes. Some target all cancers, while others target specific cancers (e.g., breast, colon, or prostate cancers). The genes on the multigene tests include high-penetrance genes related to the specific tumor (such as BRCA1/BRCA2 on a breast cancer panel); high penetrance genes related to a different type of cancer but with a more moderate risk for the tumor of reference (such as CDH1 or MSH6 on a breast cancer panel); and moderate penetrance genes for which clinical utility is uncertain (such as NBN on a breast cancer panel). Because multiple genes are included on these panels, it is anticipated that many, and perhaps most, individuals undergoing testing using these panels will be found to have at least one VUS. As it is not possible to do standard pretest counseling models for a panel of 20 genes, new counseling models are needed. Ethical issues of whether patients can opt out of specific results (such as TP53 or CDH1 in breast cancer) and how this would be done in clinical practice are unresolved.
Refer to the Multigene (panel) testing section in the PDQ summary on Cancer Genetics Risk Assessment and Counseling for more information about the use of targeted multigene tests.
WES for inherited cancer susceptibility is also commercially available. Secondary findings are likely, and management of such findings is evolving.
Governance, Interpretation, and Institutional Oversight of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
The ACCE model uses four main components to evaluate new genetic tests: analytic validity; clinical validity; clinical utility; and ethical, legal, and social issues.[17]
- Analytic validity reflects the accuracy and reliability of the measurement of the genotype.
- Clinical validity refers to how accurately the finding (such a genetic variation) predicts the outcome of interest (such as cancer risk).
- Clinical utility considers whether patient outcome is improved by knowledge of the test result. In 2015, the ACMG issued a policy statement regarding the need to expand the definition of clinical utility to consider the utility of genetic and genomic services for individual patients, families, and society.[5]
- Ethical, legal, and social issues, including informed consent issues, can arise with each new genetic test.
The ACCE model's framework has been adopted worldwide for the evaluation of genetic tests.
Several layers of complexity exist in managing NGS in the clinical setting. At the purely technical level, improvements in the sequencing technique have allowed for sequencing across the entire genome, not merely the exome. As the costs decrease, exomic and genomic sequencing of tumor and normal tissue can be expected to become more routine.
With routine use of WGS, major challenges in interpretation emerge. Foremost is the matter of determining which sequence variations in known cancer predisposition genes are pathologic, which are harmless, and which variations require further evaluation as to their significance. This is not a new challenge. Various groups are developing processes for the interpretation and curation of a growing database of variants and their significance. For example, the International Society for Gastrointestinal Hereditary Tumors has developed such a process for the MMR genes in concert with the Human Variome Project and International Mismatch Repair Consortium.
These processes may serve as a framework for the emerging challenge of interpreting the significance of sequence variations in genes of uncertain or unknown function in regulation of neoplastic progression or other diseases. Larger cancer predisposition multigene tests have been developed by commercial laboratories, with their own process for interpretation. To the extent that increasingly larger multigene tests include genes of unknown significance, governance of the interpretation process requires that academic institutions offering their own multigene tests or using external proprietary panels develop a deliberative process for managing the quality assurance for test performance (including Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments [CLIA], where appropriate) and interpretation.
ACMG has issued the following updated guidelines for achieving accountability in interpreting and reporting secondary findings:[4,18]
- Constitutional variants in a list of 56 genes should be reported by the laboratory to the ordering clinician, regardless of the indication for which the clinical sequencing was ordered and regardless of patient age. This includes the normal sample of a tumor-normal sequenced dyad. Patients may opt out of such analysis after clear understanding of the ramifications and full informed consent prior to clinical sequencing.
- Only variants previously reported and a recognized cause of the disorder, or variants previously unreported but of the type expected to cause the disorder, should be reported.
- When clinical genome-scale sequencing is performed, written informed consent should be obtained by a qualified genetics health-care professional describing the nature of the test and addressing issues such as interpretive uncertainty, privacy, familial impact, and generation of secondary findings.
- Clinicians should be familiar with basic attributes and limitations of clinical sequencing.
- ACMG, together with content experts and other professional organizations, should continue to refine and update such guidelines annually.
Concerns remain that the routine reporting of germline variants in the context of tumor sequencing would require laboratories to conduct results review with germline and tumor genome expertise, which would be expected to increase costs, laboratory efforts, and turnaround time for results reporting. The nature of discussions between oncologists and patients would be altered to include the multiple facets involved with germline testing and potential results. Pre- and post-test discussions would also potentially require involvement of genetic counselors and geneticists, who are a limited resource in oncology practices. Recent expert comment stated that more data are needed about the benefits of return of secondary germline findings to cancer patients undergoing tumor sequencing, citing a need for recommendations by experts in the oncology and genetics communities.[19]
It is still very early in the development processes for oversight at the institutional level. As an example, at one high-volume cancer center, the following process has been used:
- When considering evaluation of tumor tissue for research purposes, patients are asked to consent to undergo tests of very large panels of somatic tissue that are paired with corresponding panels for constitutional tissue. The key research undertakings involve evaluating for differences in prognosis and treatment response according to variant patterns in tumors.
- The consent process outlines the possibility that variants suggesting underlying tumor susceptibility may be identified. Patients are asked whether they want to receive this information, should an actionable genetic variant be identified. Patients also receive expedited genetic counseling (via counselors associated with the research protocol). If a patient has chosen not to receive such actionable genetic variant information, findings will nevertheless be reported to the patient’s institutional primary care physician (PCP). Unresolved to date are the circumstances in which a patient may be approached again by his or her PCP regarding pertinent findings, notwithstanding a previous decline to receive such information.
- When potentially significant results are found, the specific test may be repeated in a CLIA lab.
- A committee was formed to review variants to determine whether they are considered pathogenic or otherwise actionable.
- A second committee was formed to provide oversight for the conduct of such protocols, in the interest of deliberately evolving the processes above in a manner consistent with the anticipated routine performance of such panels in cancer patients, balanced against the need for patient autonomy and appropriately detailed informed consent.
Informed Consent Issues Arising From the Application of NGS
Informed consent for the sequencing of highly penetrant disease genes has been conducted since the mid-1990s in the contexts of known or suspected inherited diseases within selected families. However, the best methods and approaches for educating and counseling individuals about the potential benefits, limitations, and harms of genetic testing to facilitate informed decisions have not been fully elucidated or adequately tested. New informed consent challenges arise as NGS technologies are applied in clinical and research settings. Challenges to facilitating informed consent include the following:
- Providing a person-centered appreciation for the breadth and diversity of medical risks potentially identified through genomic sequencing. Establishing informed consent may be particularly challenging in medically underserved populations with less familiarity with the concept of disease risk and in individuals with no previous knowledge, experience, or context of the disease(s) for which they are identified to be at increased risk.
- Sequencing for diseases without clear management algorithms or identified best practices.
- Interpretation of variants of possible but unclear pathogenicity.
- Communicating genetic information that may be of relevance for other family members.
- Additional challenges are anticipated as health care providers not trained in genetic/genomic medicine order and receive results on behalf of their patients with the expectation to return and manage medically actionable results.
The increased availability and decreased cost of NGS technology are expanding the use of genome-wide testing of tumors, with the goal of identifying somatic variants as potential targets for cancer treatment. While identifying germline pathogenic variants may be considered secondary to the main purpose of testing tumors, the possibility of identifying actionable secondary findings of pathogenic variants in cancer predisposition genes supports the need for genetic counseling in this context. Approaches for genetic counseling and informed consent in the context of tumor sequencing have been proposed.[20,21]
Conclusion
Advances in genetic sequencing technologies have dramatically reduced the cost of sequencing an individual's full genome or exome. WGS and WES are increasingly being employed in the clinical setting in testing for both somatic variants and germline variants. In addition, multigene tests are now available commercially or within an institution. Considerable debate surrounds the clinical, ethical, legal, and counseling aspects associated with NGS and gene panels. Future research is warranted to address these issues.
References
- Dancey JE, Bedard PL, Onetto N, et al.: The genetic basis for cancer treatment decisions. Cell 148 (3): 409-20, 2012. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Meric-Bernstam F, Farhangfar C, Mendelsohn J, et al.: Building a personalized medicine infrastructure at a major cancer center. J Clin Oncol 31 (15): 1849-57, 2013. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Sleijfer S, Bogaerts J, Siu LL: Designing transformative clinical trials in the cancer genome era. J Clin Oncol 31 (15): 1834-41, 2013. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Green RC, Berg JS, Grody WW, et al.: ACMG recommendations for reporting of incidental findings in clinical exome and genome sequencing. Genet Med 15 (7): 565-74, 2013. [PUBMED Abstract]
- ACMG Board of Directors: Clinical utility of genetic and genomic services: a position statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med 17 (6): 505-7, 2015. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al.: Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 17 (5): 405-24, 2015. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Presidential Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues: Anticipate and Communicate: Ethical Management of Incidental and Secondary Findings in the Clinical, Research, and Direct-to-Consumer Contexts. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, 2013. Available online. Last accessed May 8, 2025.
- National Human Genome Research Institute: DNA Sequencing Costs: Data from the NHGRI Genome Sequencing Program (GSP). 2014. Available online. Last accessed May 8, 2025.
- Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74 (12): 5463-7, 1977. [PUBMED Abstract]
- MacConaill LE: Existing and emerging technologies for tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol 31 (15): 1815-24, 2013. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Rizzo JM, Buck MJ: Key principles and clinical applications of "next-generation" DNA sequencing. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 5 (7): 887-900, 2012. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Linnarsson S: Recent advances in DNA sequencing methods - general principles of sample preparation. Exp Cell Res 316 (8): 1339-43, 2010. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Fernald GH, Capriotti E, Daneshjou R, et al.: Bioinformatics challenges for personalized medicine. Bioinformatics 27 (13): 1741-8, 2011. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Mardis ER: The $1,000 genome, the $100,000 analysis? Genome Med 2 (11): 84, 2010. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Schrader KA, Cheng DT, Joseph V, et al.: Germline Variants in Targeted Tumor Sequencing Using Matched Normal DNA. JAMA Oncol 2 (1): 104-11, 2016. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Raymond VM, Gray SW, Roychowdhury S, et al.: Germline Findings in Tumor-Only Sequencing: Points to Consider for Clinicians and Laboratories. J Natl Cancer Inst 108 (4): , 2016. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Haddow J, Palomaki G: A model process for evaluating data on emerging genetic tests. In: Khoury M, Little J, Burke W, eds.: Human Genome Epidemiology: A Scientific Foundation for Using Genetic Information to Improve Health and Prevent Disease. Oxford University Press, 2004, pp 217-33.
- ACMG Board of Directors: ACMG policy statement: updated recommendations regarding analysis and reporting of secondary findings in clinical genome-scale sequencing. Genet Med 17 (1): 68-9, 2015. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Parsons DW, Roy A, Plon SE, et al.: Clinical tumor sequencing: an incidental casualty of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics recommendations for reporting of incidental findings. J Clin Oncol 32 (21): 2203-5, 2014. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Everett JN, Gustafson SL, Raymond VM: Traditional roles in a non-traditional setting: genetic counseling in precision oncology. J Genet Couns 23 (4): 655-60, 2014. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Catenacci DV, Amico AL, Nielsen SM, et al.: Tumor genome analysis includes germline genome: are we ready for surprises? Int J Cancer 136 (7): 1559-67, 2015. [PUBMED Abstract]
Structure and Content of PDQ Summaries
PDQ Cancer Genetics summaries focus on the genetics of specific cancers, inherited cancer syndromes, and the ethical, social, and psychological implications of cancer genetics knowledge. Sections on the genetics of specific cancers include syndrome-specific information on the risk implications of a family history of cancer, the prevalence and characteristics of cancer-predisposing variants, known modifiers of genetic risk, opportunities for genetic testing, outcomes of genetic counseling and testing, and interventions available for people with increased cancer risk resulting from an inherited predisposition.
The source of medical literature cited in PDQ Cancer Genetics summaries is peer-reviewed scientific publications, the quality and reliability of which is evaluated in terms of levels of evidence. Where relevant, the level of evidence is cited, or particular strengths of a study or limitations of the evidence are described.
Refer to the Levels of Evidence for Cancer Genetics Studies summary for more information about the levels of evidence used in the PDQ Cancer Genetics summaries.
Genetics Resources
Health care providers who deliver genetic services, including genetic counseling, can be located through local, regional, and national professional genetics organizations such as the National Society of Genetic Counselors. Providers of cancer genetic services are not limited to one specialty and include medical geneticists, genetic counselors, advanced-practice genetics nurses, oncologists (medical, radiation, or surgical), other surgeons, internists, pediatricians, family practitioners, and mental health professionals. A cancer genetics health care provider will assist in constructing and evaluating a pedigree, eliciting and evaluating personal and family medical histories, and calculating and providing information about cancer risk and/or probability of a pathogenic variant being associated with cancer in the family. In addition, if a genetic test is available, these providers can assist in pretest counseling, laboratory selection, informed consent, test interpretation, posttest counseling, and follow-up.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| ClinGen | A program to evaluate the clinical relevance of genetic variants for use in precision medicine and research. |
| ClinVar | A public archival database that aggregates information about genomic variation and its relationship to human health. |
| National Institutes of Health Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) | Central location for voluntary submission of genetic test information by providers. The scope includes the test's purpose, methodology, validity, evidence of the test's usefulness, and laboratory contacts and credentials. |
| Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) | Catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Clinical Practice Guidelines from the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) | Clinical practice guidelines developed by expert panels for risk assessment, testing, and counseling of individuals with various inherited conditions, including some cancers, or individuals with a high risk of developing these conditions. |
| Clinical Practice Guidelines from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) | Clinical practice guidelines developed by expert panels for specific clinical situations (disease-oriented) or use of approved medical products, procedures, or tests (modality-oriented). |
| Guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) | Clinical practice guidelines developed by expert panels that detail the sequential management decisions and interventions for the malignant cancers that affect 97% of all patients with cancer. In addition, separate guidelines relate to major prevention and screening topics, and another set of pathways focuses on the major supportive care areas. |
| National Guideline Clearinghouse from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) | A public resource for evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Dictionary of Genetics Terms (NCI) | Definitions of more than 200 terms related to genetics. |
| DNA Learning Center (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory) | Variety of educational resources, including an interactive DNA timeline. |
| The DNA Files | Series of 14 one-hour public radio documentaries and related information. |
| Facing Our Risk of Cancer Empowered (FORCE) | Support and information to individuals and families affected by hereditary breast and ovarian cancer through a toll-free help line, message boards, chat rooms, and support groups. |
| Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (National Human Genome Research Institute [NHGRI]) | Information service for the general public, including patients and their families, and for health care professionals and biomedical researchers. |
| Genetic Science Learning Center (The University of Utah) | Information about basic genetics, genetic disorders, genetics in society, and several thematic units. |
| Genetic Testing for Inherited Cancer Risk (NCI) | A fact sheet about genetic testing for inherited cancer risk, including types of tests, who should consider testing, how to understand test results, and who has access to a person’s test results. Also contains information about at-home or direct-to-consumer genetic tests. |
| MedlinePlus: Genetics (National Library of Medicine) | Consumer information about genetic conditions and the genes or chromosomes responsible for those conditions. |
| Talking Glossary of Genomic and Genetic Terms (NHGRI) | Contains definitions of more than 200 terms related to genetics and a quiz to test your knowledge of genetic terminology. Many terms also have images, animations, and descriptions by specialists in the field of genetics. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Bioethics Today | Links to articles on genetics and bioethics. |
| DNA Patent Database | Searchable database of U.S. DNA-based patents and patent applications issued by the U.S. Patent and Patent Applications Trademark Office. |
| Ethical, Legal, and Social Issues (U.S. Department of Energy) | Information, articles, and links on a wide range of genetics issues. |
| Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) of 2008 (National Human Genome Research Institute [NHGRI]) | Information describing genetic discrimination and GINA for the public. |
| Genome Statute and Legislation Database (NHGRI) | Searchable database of state laws/statutes about privacy of genetic information/confidentiality; informed consent; insurance and employment discrimination; genetic testing and counseling; and commercialization and patenting. |
| HumGen International | Comprehensive international database on the legal, social, and ethical aspects of human genetics. |
| Bioethics Research Library (Georgetown University) | Search engine for literature on specific issues related to ethics and human genetics. |
| National Society of Genetic Counselors Code of Ethics | A statement to clarify and guide the ethical conduct of genetic counselors. |
| Congress.gov (the Library of Congress) | Searchable database of U.S. legislation (current and previous Congresses). |
| Your Genes, Your Choices: Exploring the Issues Raised by Genetic Research | Description of the Human Genome Project, the science behind it, and the ethical, legal, and social issues raised by the project. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Does it Run in the Family Toolkit (Genetic Alliance) | Tips for collecting family history information and links to resources. |
| Family Health History (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC]) | Website devoted to using family history to promote health. The website includes a link to My Family Health Portrait, a Web-based family history tool. |
| Family History Resources (National Society of Genetic Counselors) | Information on collecting a family health history. |
| Collecting a Family History (American Medical Association) | Tools for gathering family history and links to resources. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| UCSC = University of California, Santa Cruz. | |
| Chromosomal Variation in Man | Searchable database of literature citations on chromosomal variants and anomalies. |
| Ensembl (Joint software project between the European Bioinformatics Institute and the Wellcome Sanger Institute) | Data sets resulting from an automated genome analysis and annotation process. |
| Leiden Open Variation Database | A flexible, free tool for gene-centered collection, curation, and display of DNA variation. |
| KMcancerDB | Human pathogenic variant database with graphical display of molecular information for cancer-related genes. |
| National Center for Biotechnology Information: Genome | Views of chromosomes, maps, and loci; links to other NCBI resources. |
| Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) | Catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. |
| UCSC Genome Browser | Reference sequence for the human and C. elegans genomes and working drafts for the mouse, rat, Fugu, Drosophila, C. briggsae, yeast, and SARS genomes. |
| Human Subjects Research in Genomics (National Human Genome Research Institute [NHGRI]) | Discusses many issues that continue to challenge institutional review boards, investigators, and policy makers today. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Centre for Genetics Education | Education and service resources for patients and professionals. |
| DNA Learning Center | Variety of educational resources, including an interactive DNA timeline. |
| Essentials of Genetic and Genomic Nursing: Competencies, Curricula Guidelines, and Outcome Indicators, 2nd edition | Establishes minimum basis to prepare the nursing workforce to deliver competent genetic and genomic-focused nursing care. |
| Genetics Toolkit (American Society of Clinical Oncology) | A collection of tools and resources to assist oncology professionals with integrating hereditary cancer risk assessment into practice. |
| Genetics Toolkit (Society of Gynecologic Oncology) | A series of case studies to illustrate common questions and challenges faced by health professionals and patients with regard to the role of genetics in gynecologic cancers. This resource was developed in collaboration by the Society of Gynecologic Oncology, the National Society of Genetic Counselors, Bright Pink, and Facing Our Risk of Cancer Empowered (FORCE). |
| Medical School Core Curriculum in Genetics | Medical school course competencies, skills, knowledge, and behaviors that should be covered in a genetics curriculum developed by the Association of Professors of Human and Medical Genetics and the American Society of Human Genetics. |
| NHS England Genomics Education Programme | Develops, provides, and evaluates genetics education opportunities and resources. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| American Board of Genetic Counseling (ABGC) | Information about certification of genetic counselors. |
| American Board of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ABMGG) | Information about medical genetic training programs and certification of geneticists. |
| American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) | Resources, policy statements, and practice guidelines about medical genetics. |
| American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) | Resources, projects, and policies concerning human genetics. |
| Genetics Society of America (GSA) | Links to teaching websites, general educational courses, and journals and publications about genetics. |
| International Society of Nurses in Genetics (ISONG) | Resources to help nurses incorporate new knowledge about human genetics into practice, education, and research. |
| National Society of Genetic Counselors (NSGC) | Information about genetic counseling: practice guidelines, links to genetic counselors, and genetic discrimination resources. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer Genetics Referral Screening Tool (B-RST) | A screening tool that helps to identify people who may have an increased risk of hereditary breast and ovarian cancers because of their family histories.[1,2] |
| Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (National Cancer Institute [NCI]) | Interactive tool for estimating a woman's risk of developing invasive breast cancer. |
| Colorectal Cancer Risk Assessment Tool (NCI) | Interactive tool for estimating the risk of developing colorectal cancer in a non-Hispanic White man or woman aged 50 to 85 years. |
| Family Health Risk Calculator (The Ohio State University Medical Center) | Interactive tool that estimates cancer risk by reviewing patterns of cancer in a family. |
| Melanoma Risk Assessment Tool (NCI) | Interactive tool for estimating an individual’s absolute risk of developing melanoma. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| MMR = mismatch repair; MRC = Medical Research Council. | |
| MRC Human Genetics Unit, Edinburgh | Predicts the likelihood of pathogenic variants in one of the MMR genes in persons with colon cancer. |
| PREMM5 Model: Lynch Syndrome Prediction Model for MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, and EPCAM Pathogenic Variants | Estimates the probability that an individual carries a pathogenic variant in the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, or EPCAM gene. This model replaces the PREMM(1,2,6) model. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| GWAS = genome-wide association studies; HuGE = Human Genome Epidemiology; SNV = single nucleotide variant. | |
| GWAS Catalog | An online catalog of SNV-trait associations from published GWAS for use in investigating genomic characteristics of trait/disease-associated SNVs. |
| HuGE Navigator | An integrated, searchable knowledge base of genetic associations and human genome epidemiology. |
| Bioethic Research Library (Georgetown University) | Search engine for literature on specific issues related to ethics and human genetics. |
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Public Health Genomics at the CDC | Information on how human genomic discoveries can be used to improve health and prevent disease, including links to many resources. |
| National Cancer Institute | Summaries of cancer genetics–related information. |
| National Human Genome Research Institute | Research, policy, ethics, education, and training information and resources about genetic and rare diseases. |
| U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science | Genomics educational resources. |
References
- Bellcross CA, Lemke AA, Pape LS, et al.: Evaluation of a breast/ovarian cancer genetics referral screening tool in a mammography population. Genet Med 11 (11): 783-9, 2009. [PUBMED Abstract]
- Bellcross C: Further development and evaluation of a breast/ovarian cancer genetics referral screening tool. Genet Med 12 (4): 240, 2010. [PUBMED Abstract]
Latest Updates to This Summary (05/09/2025)
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Methods of Genetic Analysis and Gene Discovery
Added American Cancer Society as reference 1.
This summary is written and maintained by the PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board, which is editorially independent of NCI. The summary reflects an independent review of the literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or NIH. More information about summary policies and the role of the PDQ Editorial Boards in maintaining the PDQ summaries can be found on the About This PDQ Summary and PDQ® Cancer Information for Health Professionals pages.
About This PDQ Summary
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary for health professionals provides comprehensive, peer-reviewed, evidence-based information about cancer genetics. It is intended as a resource to inform and assist clinicians in the care of their patients. It does not provide formal guidelines or recommendations for making health care decisions.
Reviewers and Updates
This summary is reviewed regularly and updated as necessary by the PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board, which is editorially independent of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). The summary reflects an independent review of the literature and does not represent a policy statement of NCI or the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Board members review recently published articles each month to determine whether an article should:
- be discussed at a meeting,
- be cited with text, or
- replace or update an existing article that is already cited.
Changes to the summaries are made through a consensus process in which Board members evaluate the strength of the evidence in the published articles and determine how the article should be included in the summary.
Any comments or questions about the summary content should be submitted to Cancer.gov through the NCI website's Email Us. Do not contact the individual Board Members with questions or comments about the summaries. Board members will not respond to individual inquiries.
Levels of Evidence
Some of the reference citations in this summary are accompanied by a level-of-evidence designation. These designations are intended to help readers assess the strength of the evidence supporting the use of specific interventions or approaches. The PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board uses a formal evidence ranking system in developing its level-of-evidence designations.
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. Although the content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text, it cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless it is presented in its entirety and is regularly updated. However, an author would be permitted to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks succinctly: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The preferred citation for this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Cancer Genetics Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Genetics Overview. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/pdq/information-summaries/genetics/overview-hp-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389204]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use within the PDQ summaries only. Permission to use images outside the context of PDQ information must be obtained from the owner(s) and cannot be granted by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the illustrations in this summary, along with many other cancer-related images, is available in Visuals Online, a collection of over 2,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used as a basis for insurance reimbursement determinations. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s Email Us.