Cancer Currents: An NCI Cancer Research Blog
A blog featuring news and research updates from the National Cancer Institute.
-
PDX Mouse Models Are Reliable Stand-Ins for Human Tumors, Study Finds
A large study from an international group of researchers provides reassurance that cancer models, known as PDX mice, largely retain the genetics of the human tumors from which they were created. PDX mice are increasingly used in cancer research.
-
Study Explores Jaw Problem Linked to Zoledronic Acid, Finds Risk Factors
A recent study quantified the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw for patients who take zoledronic acid to manage complications from cancer that has spread to the bone. The study also examined risk factors for osteonecrosis of the jaw in these patients.
-
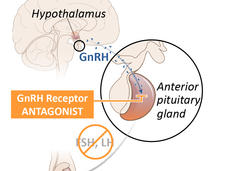
Relugolix Approval Expected to Alter Treatment for Advanced Prostate Cancer
FDA’s recent approval of relugolix (Orgovyx) is expected to affect the treatment of men with advanced prostate cancer. A large clinical trial showed that relugolix was more effective at reducing testosterone levels than another common treatment.
-
Obesity May Help Tumors Survive and Grow, Mouse Study Suggests
Obesity changed the relationship between cancer cells and nearby immune cells in ways that helped tumors survive and grow, a study in mice showed. But altering tumor cell metabolism helped immune cells once again recognize and infiltrate tumors.
-
Study Suggests a Link between Stress and Cancer Coming Back
Cancer cells that are leftover after treatment can go into a “dormant” state for years. A new study in mice suggests that stress hormones may trigger a chain reaction that wakes up dormant cancer cells, causing tumors to form again.
-
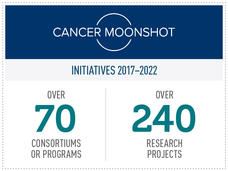
The Cancer Moonshot: A Midpoint Progress Update
With the Cancer Moonshot having reached its midway point, NCI Director Dr. Ned Sharpless and Deputy Director Dr. Dinah Singer provide a report on the progress to date and future directions for this ambitious initiative to accelerate progress against cancer.
-
Trial Tests Abemaciclib As New Option for Early-Stage Breast Cancer
The drug abemaciclib (Verzenio) may be a new treatment option for people with the most common type of breast cancer, with new study findings suggesting that it can reduce the risk of the cancer returning.
-
Steroids May Limit the Effectiveness of Immunotherapy for Brain Cancer
In people with glioblastoma and other brain cancers, steroids appear to limit the effectiveness of immunotherapy drugs, a new study shows. The findings should influence how steroids are used to manage brain tumor symptoms, researchers said.
-
Fertility Preservation Safe for Young Women with Breast Cancer
Fertility preservation for young women with breast cancer doesn’t increase their risk of dying in the ensuing decades, a new study affirmed. Experts said the findings support routinely offering fertility preservation to patients who want it.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Can Protect from Reinfection, NCI Study Suggests
In a study using data from more than 3 million people, NCI researchers have found that people who have antibodies to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, appear to have some degree of protection against being reinfected with the virus.
-
Stopping TKI Treatment Is Safe, Improves Quality of Life for Some with CML
For adults with CML who are in a sustained deep molecular remission, stopping treatment with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor is safe and improves their quality of life, a study shows. But researchers cautioned that these patients must be closely monitored.
-
Could Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs Improve Cancer Immunotherapy?
Cholesterol-lowering drugs known as PCSK9 inhibitors may improve the effectiveness of cancer immune checkpoint inhibitors, according to studies in mice. The drugs appear to improve the immunotherapy drugs’ ability to find tumors and slow their growth.
-
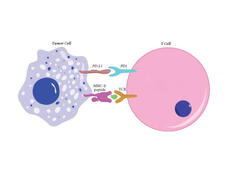
Nanoparticle Trains Immune Cells to Attack Cancer
Researchers have developed a nanoparticle that trains immune cells to attack cancer. According to the NCI-funded study, the nanoparticle slowed the growth of melanoma in mice and was more effective when combined with an immune checkpoint inhibitor.
-
Cancer “Liquid Biopsy” Blood Test Gets Expanded FDA Approval
FDA has expanded the approved uses of the FoundationOne Liquid CDx blood test, known as a liquid biopsy, that can help doctors pick specific treatments for some people with cancer. When used in this way, the test is known as a companion diagnostic.
-
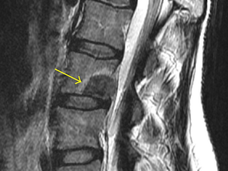
Targeted Radiation Reduces Pain from Cancer Metastases in the Spine
For some patients with painful spinal metastases from advanced cancer, a type of precise, high-dose radiation therapy—called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT)—may be a highly effective way to relieve that pain, clinical trial results show.
-
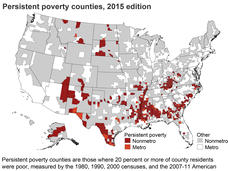
Persistent Poverty Linked to Increased Risk of Dying from Cancer
People who live in counties in the United States with persistent poverty are more likely to die from cancer than people in other counties, a new study shows, highlighting the influence of social and structural factors on health.
-
People with Cancer Say Access to Their Clinical Notes Is Valuable
People with cancer find significant value in having access to electronic clinical notes from their doctor visits, a new study shows. Expanded access to these “open notes” will soon be required under the 21st Century Cures Act.
-
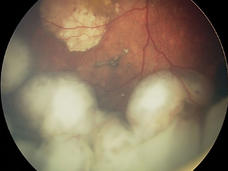
For Childhood Eye Cancer, Researchers Investigating “Packaged” CAR T Cells
For children with the eye cancer retinoblastoma, researchers are studying a CAR T-cell therapy in which the engineered immune cells are packaged in a biodegradable material called a hydrogel and then injected directly into tumors.
-
Smoking Initiation Shifting from Teens to Young Adults
The age at which people tend to start smoking has shifted upwards, with more young adults than teens trying smoking for the first time or becoming regular smokers, according to a new study.
-
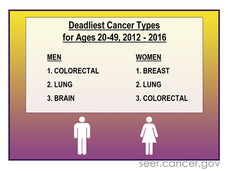
Why Is Colorectal Cancer Rising Rapidly among Young Adults?
Diagnoses of colorectal cancer continue to increase in younger adults. In September 2020, more than 400 leading scientists and patient advocates participated in an NCI/NIEHS-sponsored symposium to identify research priorities that address important questions about this concerning trend.